What is Engine? | How to Learn About Engines – [Complete Guide]
![What is Engine? | How to Learn About Engines - [Complete Guide]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/What-is-Engine-1024x539.jpg)
Engine Introduction:
What is Engine? | How to Learn About Engines – [Complete Guide]: – In the present time the engine is a collection of advanced parts and systems that give the main thrust to get you down on the road. Modern electronics and materials might have made repairing engines more complicated, yet the basic engine design has not changed throughout the year. Proper consideration and taking care of your engine will make them purr for a long time. The most ideal way to start learning about how your engine works is to break down the engine into parts and investigate each part’s function.
Engines are complex machines that power cars, bikes, planes, boats, and even factories. You could even say engine makes our entire lifestyle conceivable! They’re fascinating machines, so whether you believe that should do some car repairs or are simply inquisitive, it’s simply normal to need to look further for learning about engines.
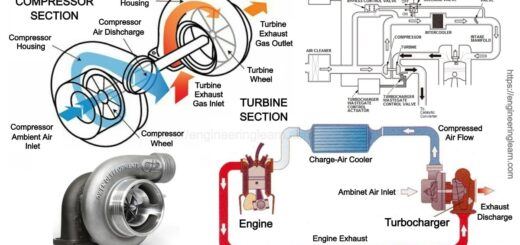
How do Combustion Engines Work?
Fundamentally, fuel enters the engine through an injector. The spark plug then ignites the fuel to deliver energy. This energy further turns the pistons in the motor, which makes the crankshaft turn. The energy then, at that point, moves to the car powertrain, which spins the wheels for motion.
This process is the manner by which an internal combustion engine works, the type that is in cars and most other motor vehicles. Be that as it may, there are different engine types, similar to steam, water, or air-powered ones.
Parts of a Combustion Engine
A portion of the parts and their jobs include:-
- Valves, which open and close the fumes and air valves to let fuel and air access the engine.
- The role of Pistons is which compress the gas to make it ignite.
- The spark plug, which ignites the gas to power the engine.
- The crankshaft, which twists or spins and delivers power.
- The engine block, is the primary support structure for the wide range of pieces of the engine.
- Combustion engines are generally arranged in a V-shape, with a row of cylinders on each side. A V6 engine, for instance, has 6 cylinders with 3 on each side.
Main Parts of an Engine
All aspects of the engine need to work properly or appropriately for it to run safely. In the event that any part isn’t working, then, at that point, the engine will either run ineffectively or fail to start altogether. The whole thing needs to remain in great working condition for the best performance for its users.
Not all car problems are issues related to the engine. For instance, in the event that your battery is dead or drained out, the engine won’t start. In any case, this doesn’t mean something isn’t quite right about your engine.
What do Combustion Engines Need to Run?
There are a few components of the combustion process that produces energy and makes the engine move. The role of injectors bring fuel and air into the engine and the further spark ignites the combination. To continue running, the engine needs a consistent supply of fuel and air, in light of the fact that the combustion process will stop without a combination of both.
A broken or grimy spark plug is a typical engine problem. Without the spark, the engine can’t turn over.
Oil isn’t part of the combustion process, however, an engine can’t work without it. On the off chance that the engine needs more oil, the moving parts will lock up and the engine won’t run. Each gas car needs to get an oil change.
Other Types of Engines
Internal combustion engines are likely what your thought process of when you consider an engine, however, there are heaps of others. The following are a couple of the other normal ones:-
The external combustion engine, where the fuel consumes in an alternate location outside the engine. A steam engine falls into this classification since the water is boiled in an alternate spot and afterward took care of the engine.
Reaction engines are also called jet engines. These spin or twist rapidly to force air out the back end, creating motion.
Electrical motors utilize electrical or mechanical energy to produce vibrations.
What’s the Best Way to Learn About Car Engines?
There are heaps of similarities between car engines, however, there could be significant differences as well. That is the reason referring to your car’s manual is the best source. This will include all the maintenance and information that is unique to your car.
(A.) The owner’s manual ought to include a diagram of your car’s engine showing its main parts, as well as maintenance information like the correct oil type.
In the event that you’ve lost the manual for your car, you can contact the manufacturer for a replacement manual. You could likewise have the option to find the manual for your car online.
(B.) Reading auto magazines and books or watching videos or recordings works as well.
Your car manual is perfect for learning the basics of your own engine, yet it has very small information about how engine work. Car magazines, books, shows, podcasts, and videos are all great sources to find out about how engines really work. These are great sources to find out about engine operation and repair.
Magazines like car and Driver or popular Mechanics have loads of great articles about engines, and cars in general. Their websites are additionally useful.
There are lots of YouTube channels focused on cars that show all the steps for any sort of engine repairs you could need to do.
It’s ideal to stay with sources made by individuals who really work on cars, similar to mechanics. Along these lines, you’ll realize the information is coming from somebody with experience.
How does a Car Engine Works?
In expansive terms, the engine can be segregated into three key parts, the head, the block, and the oil sump.
The channel through which the fuel enters the motor chamber and exhaust gases exit is called a chamber head. Its key parts are the camshafts, valves, and spark plug.
The cylinder block is where all the combustion action happens. The vital parts here are the combustion chamber, piston, and crankshaft.
One of the lowermost and essential parts of the engine is the oil slump. Its key parts are the oil pan and the oil filter.
What is the Fundamental Workflow of an Engine?
The modern-day car is a 4-stroke engine which implies it makes usable power in 4 strokes. Each stroke is characterized as the movement of the piston from the base most position to the highest position as well as the other way around. The 4-strokes are as per the following: Intake Stroke, Pressure Stroke, compression Stroke, Exhaust Stroke, and power stroke.
What are the Different Processes Inside the Engine Head?
First of all, The combustion process starts at the engine head, precisely at the intake manifold. The intake manifold is the channel through which the air-fuel combination flows into the combustion or ignition chamber. The air is directly sucked into the manifold from the choke or throttle body. The fuel, then again, is injected into the end of the manifold through a spout or nozzle called the fuel injector.
The valve in simple terms is the device or gadget that seals the chamber shut during combustion and opens the gate when fuel needs to enter the chamber or gases need to exit. The valves are open and close in view of which stroke takes place. The opening and shutting of the valves are done by an actuator rod known as the camshaft.
A round or barrel-shaped pole with drop-molded bulges is known as a camshaft. At the point when the sharp end of the cam is rotating against the valve, it pushes the valve downwards and opens up the port. Exactly when the sharp end changes from back to the round end, the valve springs push back the valve to its novel position and closed the port. The rotation of the camshaft is connected to the rotation of the crankshaft utilizing belts and pulleys. The rotation is timed or coordinated with an extremely delicate and exact timing mechanism that can be adjusted or changed manually.
What are the Different Processes Inside the Engine Block?
The combustion process takes place inside the combustion or ignition chamber present in the head. The main part is the piston. The rotational force that is generated on the wheels begins with the movement of the piston. The piston generates usable power through a sum of 4 strokes or 4 movements of the piston from one end to another. Let’s, discuss these 4 strokes exhaustively: –
#1. Intake Stroke
The combustion begins with the piston at the top right on target or TDC position. The piston now begins to move down. Not long before the piston starts its downward motion, the intake valve opens up. As the piston drops down, it sucks in the fresh air-fuel mixture from the manifold. As the piston arrives at a base perfectly on target or BDC, the chamber fills off with an air-fuel combination.
#2. Compression Stroke
When the piston has arrived at BDC, the compression or pressure stroke starts. Not long before the piston arrives at the lowermost position, the intake valve closes. Then, the cylinder moves upwards. As it climbs, it compresses the air-fuel combination as it has no place to escape with the closed valves.
#3. Power Stroke
Not long before the piston arrives at the highest situation in the compression stroke, the spark plug mounted on the cylinder head lets off an exceptionally small flash. At the point when this spark comes into contact with the compressed air-fuel mixture, it ignites the mixture. When ignited, the flame quickly expands. Since the valves are as yet closed, the flame has no place to get away and pushes the piston downwards. This is the power stroke where usable power is generated or created by the movement of the piston.
#4. Exhaust Stroke
The piston with the force acquired from the previous stroke begins to move back upwards. As it moves, the exhaust valve opens up. The extra or leftover gases from the combustion or ignition process are pushed out. With this one 4-stroke cycle is completed. After this, the piston again moves from TDC to BDC and the cycle starts again.
The piston is connected with a rotating shaft called the crankshaft through a connecting rod. The piston is connected or associated with offset projections on the rod and is called crank-pins. So it successfully changes over the overall motion of the piston into rotational motion. The crankshaft rotation arrives in the wheel passing through different components and parts on the way.
What is the Role of the Oil Sump in the Engine?
The Oil Sump is the lowermost part of the engine. The function or role of the oil sump is to store and circle the lubricant or grease oil to the different moving parts of the engine. Two essential parts are located in the oil sump, the oil container, and the oil pump. The oil pan is the reservoir where all the lubricants are stored. Submerged in this oil pan is the oil pump which sucks in oil and moves it to the oil channel.
The oil pump has a small strainer at its opening which is utilized to filter out enormous flotsam and jetsam. When the oil is sucked in by the pump, it passes the oil to a primary oil filter which eliminates all the more modest debris and metal pieces too. This oil is then passed into the lubricant channel and sprayed around the different engine parts. This oil falls back through a different channel and is sent back to the sump where the process restarts.
Conclusion
Assuming you need to replace your motor, talk about the benefits of purchasing used versus new. In the event that you anticipate saving your car for quite a while, a new engine may be the smartest choice. Once in a while new engines are not considerably more costly than modified ones and offer the best solution.
While trying to analyze engine noises, be as illustrative as could really be expected. Observe when the noise occurs, at what throttle position, and when the noise started occurring. In some cases changing the weight of the oil being utilized can cause another new noise to crop up. Ensure your mechanic knows whether you changed oil brands or weight as of late.
Content Source: – cars24, wikihow, autoeducation
Image Source: – greencarreports