What is an Anchor Bolt? Types of Anchor Bolts, Applications, Uses & Selection [With Pictures]
![What is an Anchor Bolt? Types of Anchor Bolts, Applications, Uses & Selection [With Pictures]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Anchor-Bolt-1024x539.jpg)
Introduction
What is an Anchor Bolt? Types of Anchor Bolts, Applications, Uses & Selection [With Pictures]: – Anchor bolts append and secure structural elements or components to substantial structures. As a general rule, anchor bolts are utilized to secure skids, hardware, and structural members to concrete. One end of the anchor bolts is implanted in the concrete, while the opposite end is kept uncovered or exposed. The exposed end is normally threaded to attach structural elements or the equipment. ( Types of Bolts )
What is an Anchor Bolt?
Anchor bolts are designed to attach structural elements or components to concrete. In many industries, anchor bolts are typically used to attach or append steel to concrete. One end is installed into the concrete, while the opposite end is threaded to attach primary support. A mechanical fastener that connects numerous objects to a concrete surface is known as an anchor bolt. A Civil engineer or specialists frequently use these heavy-duty fasteners. Anchor bolts have a specific design that keeps equipment and structures protected in place.
Selection of Anchor Bolt
At the point when you connect or interface a piece of equipment to concrete, it ought to hold for a lifetime. For that reason, it is essential to select the right anchor bolts for your application. There are many issues to consider while choosing an anchor bolt to fasten an object to a substantial structure. Selecting or picking the correct anchor bolt relies upon several elements.
Some of the essential or fundamental factors to consider while selecting anchor bolts are:
- Anchor bolt hole size: As the diameter or distance increases, so does the load-carrying capacity.
- Anchor bolt length: The more profound the embedment within the concrete, the more noteworthy the greater the load-bearing power. The effective or powerful embedment length should be more than (4*d) or 2.
- The base material of the object.
- The design’s natural conditions
- The most extreme burden or weight that the anchor can endure
- Type of load: The holding capacity of anchor bolts reduces or decreases with vibrating and shocking loads.
- The material strength of the anchor bolt.
- Type or Sort of the concrete
- The size and position of the fittings
- The ideal appearance of the finished product
- Anchor spacing necessity or requirement.
Types of Anchor Bolts
Contingent upon the installation necessities, Anchor bolts utilized in industrial ventures are categorized into the accompanying two groups:
- Cast-in-Place anchor bolts and
- Post-Installed anchor bolts
A) Cast-in-Place Anchor Bolts
From the name itself, it is very certain that the cast-in-place anchor bolts are projected directly into the concrete material. They are the least complex yet the most grounded of all anchor bolts utilized. This kind of anchor bolt is placed in the wet concrete that turns out to be fully secured when the concrete fixes and solidifies.
Anchor bolts of cast-in-place types are again arranged into different groups. The most widely recognized sorts of cast-in-place anchor bolts are:
1. Bent-bar Anchor Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )
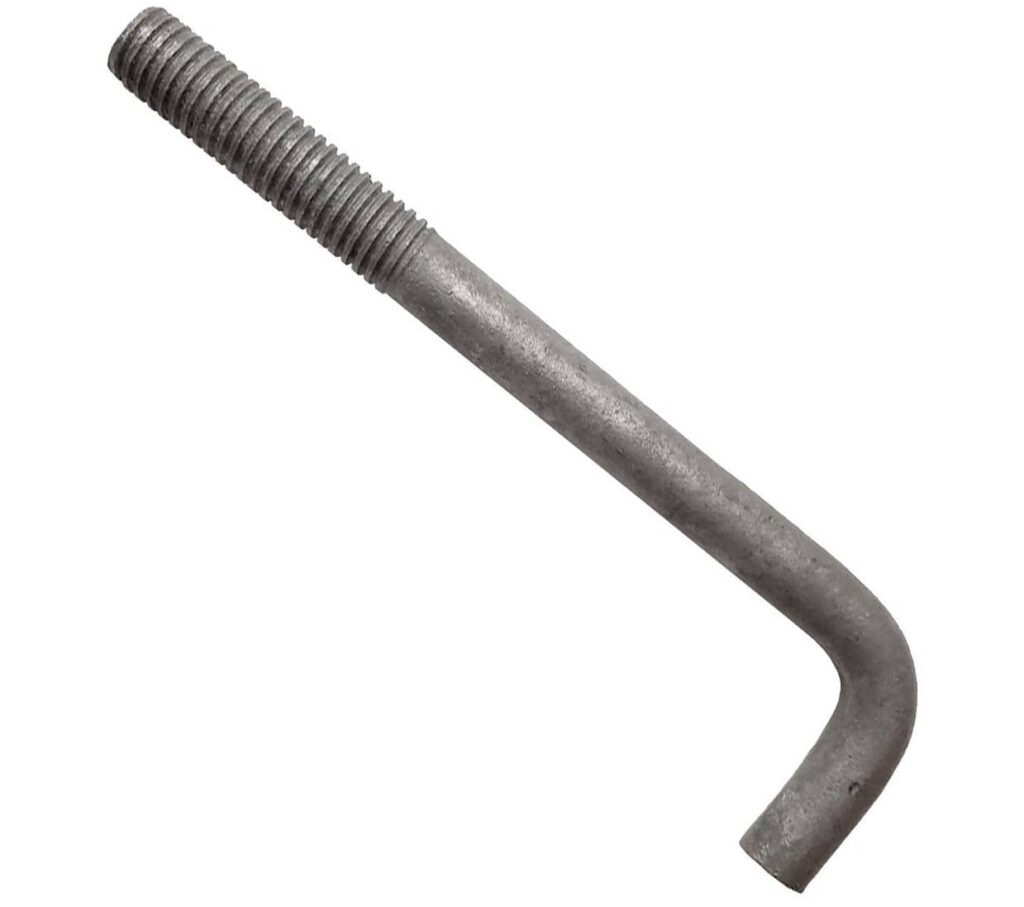

These are fundamentally steel rods or bars bent into one or the other L or J shapes. These types of anchor bolts have threads toward one side with the other bent end bowed is embedded into the concrete. J-bolt and L-bolt anchor bolts are very common in signposts, shafts, heavy hardware, tooling, and other steel structures.
2. Drop-in Anchor Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )
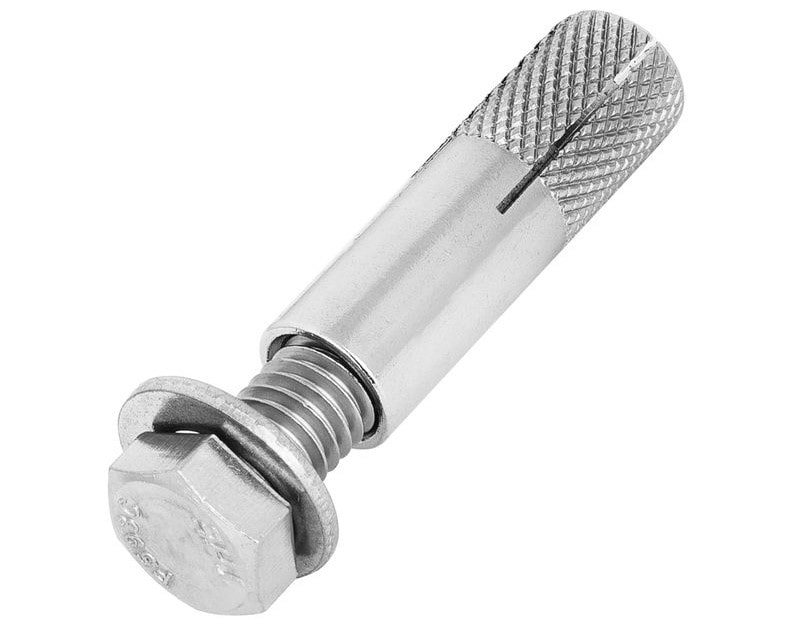

Drop-in bolts are quite basic and straightforward. At the point when the concrete section is wet, a cork-screwed sheath is embedded or inserted into the blend keeping it flush with the slab surface to insert or embed a matching bolt when the mixture or combination dries.
3. Sleeve Anchor Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

Looking like standard drop-in anchors, Sleeve anchor bolts are essentially utilized in bricks and have a more drawn-out length.
4. Headed Anchor Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )
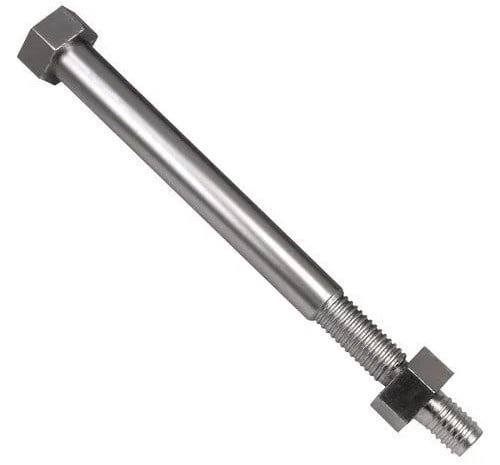

Headed anchor bolts have a forged hexagonal or square head toward one side which is implanted or embedded in the concrete. These bolts have a forged head toward one side, typically designed as a hex, or a square head. The head embeds into the concrete. On the off chance that a metal plate welds to each side of the bolt, they are categorized as plate anchors. These plate anchors are still classified as headed anchor bolts. These sorts of fasteners give or provide a decent look at the surface without the distending nut and fastener.
5. Plate Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )
Plate bolts usually or ordinarily comprise a T-shaped bolt mounted upside down into wet concrete. The “T” end of these bolts or fasteners is furnished with a corkscrewed section for mounting a nut and a circular plate. This type of anchor bolt is otherwise called a Double End rod with Plate. The plate is typically welded to the anchor bolt or a nut is implanted in the concrete.
6. Swedge Bolts: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

They are fundamentally or basically a round bar with thread toward one side and “swedged” on the other. The term “swedge” connotes the numerous indention made on the bar to get a superior grip on the concrete. This sort of anchor bolt is commonly utilized in the construction and development of girders and piers
B) Post-Installed Anchor Bolts
Post-installed anchor bolts are installed after the concrete has previously been laid down at the site. In this sort of anchor bolt, a hole or opening is required to be bored into that concrete surface and the screw is installed. Some common post-installed anchor bolts are as follows:
2. Lag Screw: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

This kind of anchor bolt is very like the plastic wall anchors and quite easy to install. The lag Screw mounting framework utilizes a metal sheath that extends or expands when the lag screw is embedded into it.
2. Toggle Wing: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )
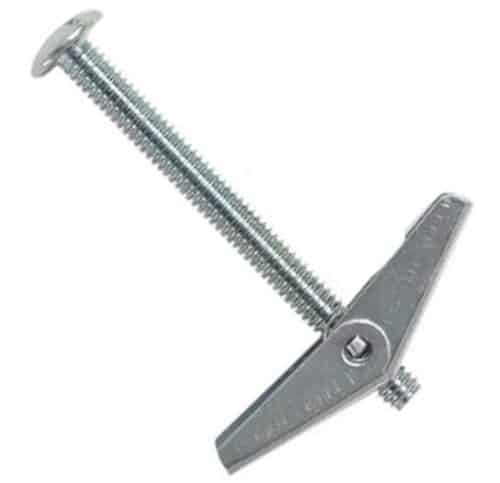

A Toggle wing is good while working with a hallow or empty wall. This sort of anchor bolt has a long-corkscrewed bolt with a pivoted wing mechanism. Both of them are embedded through a Pre bored hole for combination. The wings expand or extend in the wake of going through the hole. They are utilized for holding smaller weights.
3. Hammer Driver Pin: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

Looking like a specialty nail, hammer driver pins are utilized for mounting thin or dainty materials onto concrete. The anchor contains a skinny or thin metal sheath for inserting into the floor before being filled or loaded up with a hammer driver pin.
4. Double Expansion Shield: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

A Double or twofold expansion shield anchor bolt utilizes two parallel expansion focus points inside a customary protected anchor point. This sort of anchor bolt doubles how much contact between the sheath and the material which in turn reduces the pressure at each point.
5. Wedge Anchor Bolt: ( Types of Anchor Bolts )

Wedge Anchor bolts comprise a specific bolt featuring a moving wedge device at its base. Along these lines, these types of anchor bolts fix up towards the fastening nut, and the nut is being fastened descending toward the surface level. Contingent upon the working philosophy anchor bolts is classified into two types. They are mentioned below: –
(i) Mechanical Anchor Bolts
Utilize the frictional force or power to fix themselves in location. When installed, the mechanical anchor bolts expand which grips the base material firmly and act as an anchor.
(ii) Chemical Anchor Bolts
Chemical anchor bolts give greater adaptability and flexibility when contrasted with mechanical anchor bolts. In this kind, a resin is infused into the hole prior to inserting the stud. The chemical resin fills all irregularities of the hole and makes it waterproof and impenetrable. The bond produced by chemical anchor bolts is more grounded than the base materials.
Some examples of chemical anchor bolts are:
- Polyester chemical anchors
- Vinylester chemical anchors
- Epoxy acrylate chemical anchors
- Pure epoxy standard anchors
- Resin anchors
- Chemical threaded anchor rods
- Powder-actuated anchors
- Hybrid chemical anchors
Double End Rods with Plate
These sorts of anchors take as twofold-ended rods with a plate washer toward one side. The plate frequently welds to the anchor bolt itself, or welds to a nut embedded in concrete. Plate bolts see common use in constructing structure segments street signs, light poles, and different structures.
Applications of Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts fasten and connect structural and non-structural parts to concrete. They are used in essentially every sector. Anchor bolts are generally utilized in the following industries: –
- For repairing or fixing various parts of equipment, support establishments, and other structural parts in the chemical, petrochemical, and oil and gas industries.
- Power and Steel Industry
- Construction Industries.
- Rail lines and the airplane industry manufacturing plants and Pipeline enterprises.
- Pharmaceutical and food processing plants.
- The nuclear industry.
Causes of Anchor Bolt Failures
Any of the accompanying failures situations can cause anchor bolts to fail:-
- Tensile loads cause anchor bolt steel to break, pull out from the opening, and have different issues.
- Concrete edge failures, steel failures, and pry-failure are all instances of shear loads.
- Due to the combined or joined impact of tensile and shear loads.
What is the difference and link between anchor bolts and bolts?
- The anchor bolt is a sort of bolt connection type, and furthermore, there are a few types of bolt link forms.
- The anchor bolt is that the screw part, as well as the concrete base material, cannot be divided or separated by some form of dealing with. The detachable just nut: and the bolt, the nut is screwed off from the bolt, and the two components can be divided. It is a removable association.
- Anchor bolt is a post-anchor innovation, you need to drill or bore first, after that screw into the screw for securing; bolts are pre-formed.
- The head or top of the anchor bolt is hidden or concealed in the concrete base product, as well as the head of the bolt is subjected to the outside. The anchor bolt and the bolt are summarized: the anchor bolt is only one of the association types of the bolt.
Considerations When Deciding Anchor Bolts for the Job
Anchor bolt designs and configuration incorporates the bolt coming through the fixture. The length of the bolt extending through it depends on how frequently it should be tightened and the way that the nut was located in the concrete before the bolt was put in place. For a finished look, utilize a uniform-headed anchor bolt. Flat or round-headed sleeve anchors have smooth heads that distend from the installation and look consistent. You could likewise utilize female anchors, for example, single and twofold extension secures, machine screw anchors, or drop-in anchors to accomplish a similar look.
While considering the weight of the load that anchors must hold, it’s critical to comprehend that the bolt is the most vulnerable connection in the substantial primary framework. In view of this, decide the necessary distance across the anchor bolt put together depending on the weight that’s held. The strongest and most profound set anchor bolts with the largest diameters fit heavy loads fastened to the concrete.
(A) Vibration Loading
Equipment bonded to concrete experiences the same vibrations that the equipment does during the activity. An equipment vibration trademark requires autonomous assessment before installation. Vibrating structures incorporate pumps, engines, fans, moving belts, or even signs blowing in the breeze.
An anchor bolt transfers the shear and tension applied to it through friction however if lessens from nonstop vibration, its holding power will be decreased. In such cases, a more grounded, greater, and more profound anchor bolt ought to be utilized.
(B) Shock Loading
Any equipment fastened to the concrete where there is a shock load needs to withstand load changes throughout some undefined time frame. A typical illustration of a shock load would be a bumper on a dock. Since mechanical anchors can provide holding values in view of the friction of the bolt against the walls of the hole, assuming the friction is broken, the holding value will decrease. Shock loads may gradually loosen the anchor bolts over the long haul.
Conclusion
There is a wide range of characteristics when choosing the right anchor bolt for your application. The type and strength of the concrete, the apparatus size and location, the kind of climate, and the desired look of the finished product warrant consideration. The right measuring and spacing of anchors are basic in any structural application. Thus, planning the design of the structure in discussion with an expert underlying engineer is critical.
It’s essential to decide the overall responsibility regarding anchor bolt design. Oftentimes, numerous fabricators deliver equipment to a solitary site. Responsibility regarding anchor bolt design and deliver for the most part ought to lie with the organization accused of by and large designing liability. To finish this task effectively, equipment suppliers just should deliver equipment details like weight, height, and focus of gravity to the supplier charged with packaging.