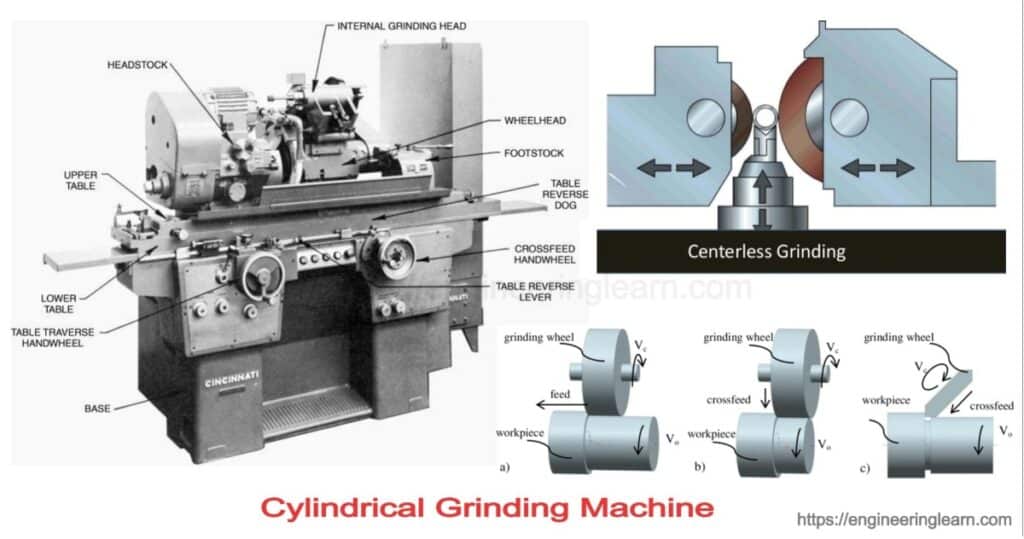
Cylindrical Grinding Machine: Types, Process & Working Principle
What is Cylindrical Grinder?
Cylindrical Grinding Machine: Types, Process & Working Principle :- Cylindrical grinders are employed to slice or cut very precise and subtle finishes on materials such as aluminum, carbide, steel or other metals. They are especially used to work on cylindrical surfaces, rods or other cylindrical work pieces. The cylinder lays in the middle of tow centers and turns in one direction whereas the grinding wheel approaches in the opposite direction.
The working of a cylinder grinder is very much similar to lathe. The only difference is that the lathe uses stationary cutting equipment whereas the grinder uses a grinding wheel. The cylinder grinders grind the materials having a central axis of rotation, for example crankshafts.
In addition to turning the work piece swiftly opposite to the grinding wheel, both the wheel and the table on which the work piece lays experience diverse movements. The grinding wheel moves up and down or side to side and the table moves backward and forward. Cylindrical grinding gives high precision and provides a superb final finish.
Types of Cylindrical Grinding Machine
1. Inside Diameter Machine
The inside diameter machine employs a collet for grinding the interior of the substance. This cylindrical grinding machine applies a wheel that is smaller than the width of the substance.
2. Outside Diameter Machine
The outside diameter machine employs centers for grinding the external surface of the substance. The centers turn the object when the object progresses through the grinding wheel.
3. Plunge Grinding Machine
The plunge grinding machine is a type of outside diameter machine. In the plunge grinding machine the grinding wheel moves radially towards the substance.
4. Creep Feed Grinding Machine
The creep feed grinding machine eliminates a full chunk of the substance through the grinding wheel all at once. This machine greatly reduces the manufacturing time.
5. Centerless Grinding Machine
The centerless grinding machines do not use centers or a collet to grip an object. These machines employ a regulating wheel placed opposite to the grinding wheel.
Types of Cylindrical Grinding Process
There are basically two types of cylindrical grinding Process-
1. External Cylindrical Grinding
External cylindrical grinding is very common grinding processes. This grinding is mainly employed for grinding rotationally symmetrical work pieces. There are different methods of external cylindrical grinding depending upon the type of work piece clamping and feed directions:
- Peripheral-cross grinding between centers (plunge grinding)
- Peripheral-longitudinal grinding between centers (oscillation grinding)
- Centre less-peripheral-cross grinding (center less plunge grinding)
- Centre less-peripheral-longitudinal grinding (center less through feed grinding)
The most common sort of clamping in external cylindrical grinding is between centers. For external cylindrical grinding extended, hefty or slim work pieces must be additionally held by stable rests so as to meet the required geometry and forms.
2. Internal Cylindrical Grinding
Internal cylindrical grinding is one of the toughest. There are different methods of internal cylindrical grinding, mainly-
• Peripheral-cross grinding (plunge grinding), and
• Peripheral longitudinal grinding (oscillation grinding)
The cause for the difficulties in internal grinding operations are the huge contact arcs in the contact zone between the grinding wheel and the work piece bore, a vibration behavior of the components involved in the active grinding process (high-frequency spindle, mandrel for the grinding wheel, work piece and bore geometry) which is problematic to control.
Working Principle of Cylindrical Grinding Machine
A cylindrical grinder is composed of four parts:
- Head and tail stocks
- Grinding wheel
- Wheel head
- Table
The work piece is gripped between the headstock and tailstock. The work piece is rotated at a fast speed between the centers. The grinding wheel, does the actual grinding by turning at a varied speed from the work piece in the opposite direction, is connected to the wheel head, which moves the grinder in different patterns such as plunge or traverse movements. At the same time, the table also moves in the lateral direction.
Image Source :- slideshare, researchgate, hkdivedi