Ignition Coil: Definition, Types, Working Principle, Construction & Problems Symptoms
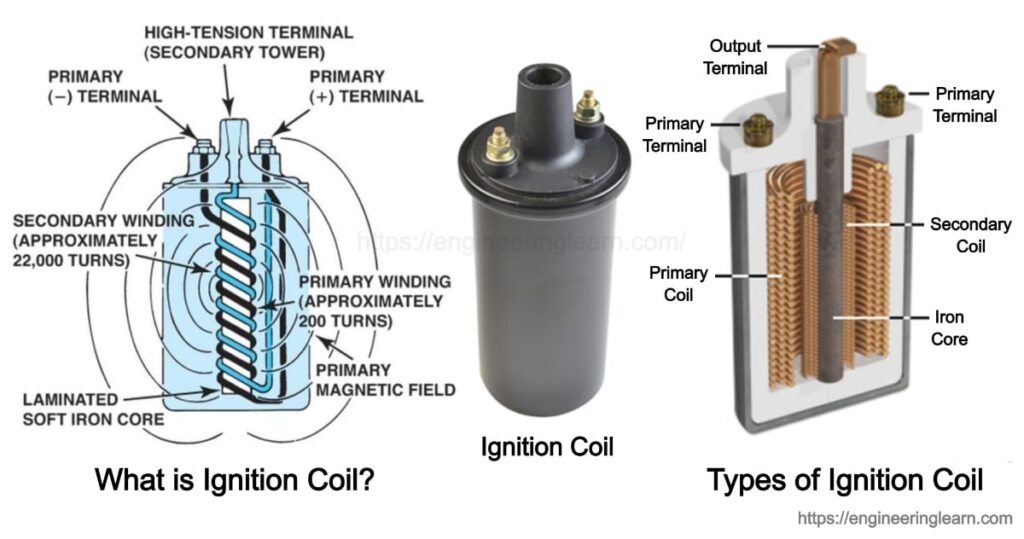
What is Ignition Coil?
Ignition Coil types and problems symptoms :- An ignition coil which is commonly known as a spark coil is an induction coil used in an automobile ignition system that converts the cell voltage to a huge voltage. This voltage is required for the formation of an electric spark in a spark plug to burn the fuel. Some coils have an inbuilt internal resistor as other coils are having external resistance to limit current. The high voltage wires that cross through the ignition coil to the distributor and then through the distributor to each of the spark plugs are called spark plug wires.
Mechanical contact breaker points and a condenser are required in every ignition system. In today’s time, a power transistor is used by an electronic ignition system to provide pulses to the ignition coil. Diesel engine depends on compression to ignite the fuel/air mixture do not need an ignition system
Working Principle of Ignition Coil
- An ignition coil made up of a layered iron core surrounded by two copper coils. It is different from a power transformer as in this there is an open magnetic circuit. The energy which is collected in the core’s magnetic field is the same energy that is given to the spark plug.
- The primary winding has lesser heavy wire turns. The secondary winding has many turns made up of smaller wire. the enamel and layers of oiled paper insulation insulate the windings from the high voltage. The coil is fitted into a metallic can with high voltage insulated terminals and low voltage connections. When the contact breaker off, it permits the battery current to flow through the primary winding of the ignition coil. The flow of the current is not so quick because of the coil inductance.
- The magnetic field is produced in the core and in the air surrounding the core by the flow of the current. The current must flow for the time to store sufficient energy in the field for striking the spark. Once the current is up to its full capacity, the contact breaker turns on. A tuned circuit is formed by the primary winding and the capacitor, and the stored energy vibrates between the inductor developed by the coil and the capacitor, the varying magnetic field in the core of the coil induces a high voltage in the secondary of the coil.
Electronic ignition systems
Modern electronic ignition systems operate on the same principle, but some depend on charging the capacitor to around 400 volts rather than charging the inductance of the coil. The timing of the switching of the transistor should be overlapped with the location of the cylinder piston so that the spark clocked to ignite the air/fuel mixture to obtain the more angular momentum possible. There are many degrees before the piston arrives at the top dead Centre. The contacts are runs a shaft that is controlled by the engine camshaft, or, the timing of the pulses is controlled by the sensor on the engine shaft whenever electronic ignition is used the amount of energy in the spark needed to strike the air-fuel mixture changes depending on the pressure & mixture, the speed of the engine.
Ignition Coil Construction
Ignition Coil types and problems symptoms :- In the earlier time, ignition coils were made with paper insulated high-voltage windings and varnish, fixed into steel can which is filled with oil for insulation and water protection. In modern automobiles, Coils are cast in filled epoxy resins which enter any air gap in the winding. Today’s single spark systems have one coil for one spark plug. To avoid early sparking at the beginning of the primary pulse, a secondary spark gap is placed in the coil to stop the reverse pulse.
The secondary windings have two terminals that are separated from the primary, and each terminal connects to a spark plug. By this, no extra diode is required as there will no fuel-air mixture present at the spark plug. Fewer primary turns are used which make the primary current higher in the low inductance coil. Solid-state switching is used because it is not compatible with the ability of mechanical breaker points
Modern Ignition Systems
In modern systems, the distributor is not permitted and ignition is preferred to be controlled electronically. Small coils are being used with a single coil per spark plug. These coils may be mounted from anywhere or they can be installed on top of the spark plug which is known as Direct Ignition. Where one coil works for two spark plugs that are two cylinders. In this arrangement, the coil produces two sparks per cycle to both cylinders. The fuel in the cylinder that is almost finishes and compression stroke is ignited, whereas the spark in its partner that is almost the end of its exhaust stroke which does not affect.
The wasted spark system is more stable than a single coil system with a distributor and cheaper than a direct ignition. When the coils are individually applied per cylinder, they all are kept in a single mounded block with various high-tension terminals. This is called a coil pack. A bad coil pack will result in bad fuel consumption or loss of power.
Ignition Coil problems symptoms
There are bad ignition coil symptoms:
- Backfiring
- Fuel Economy
- Vehicle Stalling
- Engine Jerking, Rough idling, Poor Power
- The engine does not start
- The vehicle failed to start
- Poor acceleration or loss of power
- The engine control unit shifts to home mode
- Engine fault codes
- If the coil malfunction causes failure, then this will permit raw fuel to enter; permanently degrading the catalytic converter. To avoid engine damage we will take steps to check the oil leaks and spark plug issues
- The most common cause is an oil leak from the valve cover gasket. in many types engines, the spark plug and ignition coil are mounted under a spark plug tube. Around the division of the valve cover, This tube is fixed. after a years time, the seal between the valve cover & spark plug tube can break which cause oil leak and spread around the spark plug and ignition coil which is a reason for spark plug and ignition coil failure.
- Signs of disappointed ignition coils somewhere depend on the automobile system. If a vehicle having a single coil supporting the whole engine, then the engine will not work at all as the ignition coil collapses. This can appear suddenly. Vehicles having coil-on-plug ignition system, a bad ignition coil can create a misfire in one or more cylinders simultaneously. However, The engine will run but it will rough performance. Some coil-on-plug ignition coils command two cylinders by a waste spark system. In that type of system, some unusual mishappening takes place.
Types of Ignition Coil
Ignition coils are of four types;
- Conventional Ignition Coil
- Electronic Ignition Coil
- Distributor-less Ignition Coil (DIS)
- Coil-on-Plug Ignition Coil (COP)
1. Conventional Ignition Coil: ( Types of Ignition Coil )
In a conventional breaker, point-type ignition system; the battery provides power to the primary circuit. Current passes through the windings of the primary coil and create a magnetic field. the current’s electrical circuit is broken when the points are opened. Which result in settling the magnetic field. The settled force crosses the windings of the secondary coil and creates an electrical current between them.
The current flows through the distributor cap and finally into the spark plugs in few seconds. These earlier mechanical distributor systems had their weaknesses. The ignition points got to break down and change spark timing which decreases the engine efficiency. which cause to replacement
2. Electronic Ignition Coil: ( Types of Ignition Coil )
This ignition having most of the characteristics same as that of a conventional system. But in the place of a distributor cam and points, there is the electronic system that needs a pickup coil to signal the control module. Distributor shaft manages to develop a specific amount of “lash” after miles. So gear wear always be an obstacle to proper spark timing and the development of mechanical ignition systems is required.
3. Distributor-less Ignition Coil (DIS): ( Types of Ignition Coil )
In the distributor less ignition coil, its design permits more energy to be accessible through many coils. In a coil pack, there are three or more mounted collectively.
It uses a magnetic triggering device to find engine speed and crankshaft location. This system finds spark timing based on, two shaft location sensors and a computer. Crankshaft position sensors every time monitor both shafts’ locations and feed that information into a computer.
4. Coil-on-Plug Ignition Coil (COP): ( Types of Ignition Coil )
The coil-on-plug (COP) ignition system unites all the electronic controls that can be seen in a direct ignition system. But, in the place of two cylinders dealing a single-coil, each (COP) coil cooperates with only one cylinder. As a result, some (COP) ignition systems produce as much as 47,000 volts and much hotter sparks.
Finally, the Top Failure Reasons of coil on plug ignition coils:
Bad spark plugs
Bad plug wires
Voltage overload
Image Source :- slideplayer,