What is a Flywheel? – Types, Parts, Function, Materials, Applications, Working Principle, Advantages & Disadvantages
Introduction
What is a Flywheel? – Types, Parts, Function, Materials, Applications, Working Principle, Advantages & Disadvantages: – A flywheel is one of the main parts of a vehicle engine. A mechanical device is explicitly designed for storing rotational energy (kinetic energy). It’s relative to the square of its rotational speed and mass.
The flywheel gives mass to rotational inertia to keep your vehicle engine running. If not, the engine will slow down when you let your foot off the accelerator. It balances the engine. A flywheel is explicitly weighted to the vehicle’s crankshaft to streamline the rough inclination brought about by even a slight imbalance.
What is a Flywheel?
A flywheel is basically an extremely heavy wheel that takes a lot of force to spin around. It very well may be a large-diameter wheel with spokes and an extremely heavy metal rim, or it very well may be a smaller-diameter cylinder made of something like a carbon-fiber composite. A flywheel as a weighted wheel requires adequate forces to rotate on its axis. It opposes changes in rotational speed by their moment of inertia. Changing the stored energy on the flywheel, its rotational speed should be increased or diminished. That is, it continues to spin until lots of force is applied.
A lot of kinetic energy is preserved when there is a rotation of flywheel. This energy is subsequently used to power up the vehicle while starting the engine or speeding.
How is a Flywheel Constructed?
Due to the durability necessity of a flywheel, it is normally made of steel that rotates in an conventional orientation. High-energy density flywheels are made of carbon fiber composites and utilize magnetic bearings.
What are the Applications of a Flywheel?
Its main objective is to smooth the power generation of an energy source. for example, the flywheel is utilized in reciprocating engines on the grounds that the active force from the individual piston is broken.
Flywheel is generally applied in energy storage systems to keep up with the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Providing energy at higher rates than the limit of the energy source. This is done by getting energy in a flywheel after some time. Then, at that point, releasing it rapidly at rates that surpass the energy source’s capabilities.
It is valuable in controlling the adjustment of a mechanical framework, gyroscope, and reaction cycle. Flywheel is utilized with a motorized generator to store energy. More often than not flywheel is utilized in wind turbines and auto vehicle engines. They are utilized in electric cars to support speed and in large power grids for protection from blockages. Additionally, the flywheel is utilized in advanced locomotive propulsion systems and innovative.
4 Different Types of Flywheels
1. Solid Disc Flywheel
A solid disc flywheel is a sort of Flywheel. It is utilized in singles flywheel thresher, which is made of cast iron. The solid disc Flywheel is equipped with a hub and disc. In the design estimations of a solid disc flywheel, different parameters are utilized as inputs. This incorporates the dimensions of the solid disc Flywheel.
2. Rimmed Flywheel
A rimmed-type wheel will explode at a much lower rotary speed than a solid disc-type wheel of a similar weight and diameter. For minimal weight and high energy-storage capacity, flywheels can be made using high-strength steel and produced as a tapered disc, which is thicker in the center.
3. Low-Velocity Flywheel
The angular velocity of these sorts of Flywheels comes up to 10000 rpm. They are bulky and heavy whenever compared with high-velocity Fly wheels. They need periodic maintenance and don’t utilize magnetic levitation bearings. Their installation needs exceptional substantial construction to support its weight. They are less expensive in comparison with high-velocity Fly wheels.
4. High-Velocity Flywheel
The high-velocity(speed) Flywheel has a speed between 30000 rpm to 80000 rpm. They have magnetic levitation bearings and require little support and maintenance. With regards to Size/capacity, they are lighter in weight than low-velocity flywheels. They are more costly than low-speed flywheels.
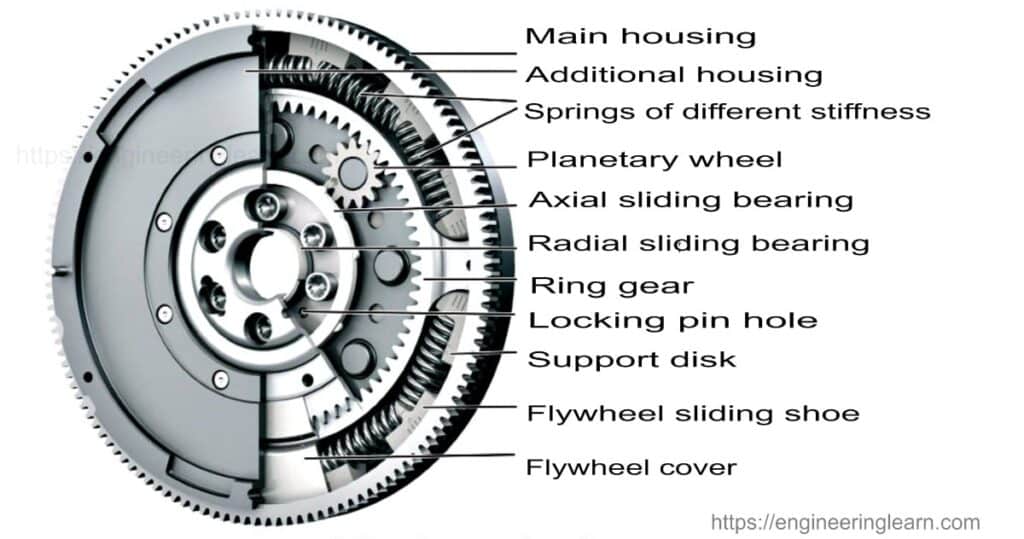
Parts of a Flywheel
(i) Flywheel Housing
The flywheel housing is solid and sits outwardly opposite the Flywheel. The flywheels are the part of the motor that twists and gives power to the alternator.
(ii) Planetary Wheel
A planetary wheel consists of a few planetary gears fixed on a flywheel section. At the point when the flywheel bracket is driven by a screw and rotates, each planetary gear meshing with the outer ring gear generates a compound motion made out of revolutions and pivots.
(iii) Ring Gear
A ring gear is mounted in the external measurement of the Flywheel. It is normally attached to the Flywheel through an interference fit, which is prepared by heating the ring gear.
(iv) Springs
The Flywheel is made out of two-stage bent springs in parallel. The outer arc is acclimated to raise the spring when the engine is running. The soft outer arc spring only serves to rectify the thunderous frequency range.
(v) Axial and Radial Sliding Bearing
Though an axially acting bearing serves just for weight remuneration, unevenness or parasitic radial forces introduced by the engine or generator unit should be redressed.
(vi) Flywheel Sliding Shoe
Sliding shoes preferably have a convex radial exterior that is on the internal mass of the flywheels. Here, they are ideally manufactured to promote slip and get through the minimal proportion of mileage.
(vii) Support Disc
Support discs are attached or joined within the Flywheel to help the two-stage bent springs and different parts of the Flywheel.
(viii) Flywheel Cover
The flywheel cover is normally made of chrome. These chrome-plated flywheel covers will hold dust back from getting into the internal workings of the Flywheel, making it run ineffectively.
(ix) Web or Arms
The web or arms are the supporting structure. It upholds the rim against the vibrations caused because of the rotation. The deciding factor of whether the flywheel ought to be an arm type or a web type relies upon the size of the flywheel.
(x) Rim
The outer circular disc of the flywheel is known as the rim. The rim is made heavier than the internal body this is to provide a superior kinetic energy transfer. The rim likewise has teeth on the external surface with mesh with the electric engine and helps in the turning over of the engine.
(xi)) Bore
The bore of the flywheel is a hole or opening made with a keyway to fit the driving shaft in it.
What does a Flywheel do?
There is a traction engine with a large flywheel that sits between the engine producing the power and the wheels that are taking that power and moving the engine not too far off. Further, The flywheel can do three exceptionally valuable jobs for us.
In the first place, in the event that the steam engine produces power intermittently, the flywheel assists with streamlining the power the wheels get. So while the engine could add power to the flywheel like clockwork, the wheels could take power from the flywheel at a consistent, continual rate and the engine would roll flawlessly as opposed to jerking along in fits and starts.
Second, the flywheel can be utilized to slow down the vehicle, similar to a brake however, a brake absorbs the vehicle’s energy as opposed to squandering it like a normal brake. Assume you’re driving a traction engine down a road and you out of nowhere need to stop. You could separate the steam engine with the clutch so the vehicle would begin to slow down. As it did as such, energy would be transferred from the vehicle to the flywheel, which would get a move on and continue to turn. You could then withdraw the flywheel to make the vehicle stop completely. Next time you set off, you’d utilize the clutch to reconnect the flywheel to the driving wheels, so the flywheel would give back a significant part of the motor it consumed during braking.
Third, a flywheel can be utilized to give brief additional power when the engine can’t produce enough. Suppose the flywheel has been spinning for quite a while yet isn’t as of now connected with either the engine or the wheels. At the point when you reconnect it to the wheels, similar to a subsequent engine gives additional power. It just works briefly, notwithstanding, on the grounds that the energy you feed to the wheels should be lost from the flywheel, making it delayed down.
What are the Functions of a Flywheel?
Flywheels can be found in practically all sort of automobiles as they fill different needs as discussed below:-
1. Engine Balancing
Since the pistons are counterbalanced from the center of the crankshaft vibration and wobbles happen. This is likewise a result of every piston firing at an alternate angle. The function of a flywheel in this present circumstance is to suppress the side-to-side motion. This is accomplished or achieved because of the heavy weight of the flywheel. Flywheels lessen the vibration of the engine however an entire engine may be settled and balanced on the mounts.
2. Drivetrain Stress Reduction
It is one more function of a flywheel, accomplished by stabilizing the engine’s movement. It additionally smooths out the engine’s speed and lessens mileage on the drivetrain parts. Flywheel likewise restricts the wear between the transmission shaft and the driveshaft. Both are connected with a universal joint.
3. Engine Start
The flywheel assumes one more part while starting the engine. The gear teeth on the flywheel are attached to a starter engine. This starter engine is controlled with the car key so when the car is started the starter motor turns the flywheel. Immediately the engine spins, and the combustion effect keeps turning the engine. The Bendix gear in the started motor pulls out for the flywheel to freely spin.
4. Engine Speed Soothing
The crankshaft changes over the piston movement into rotary motion which is jerky as the power is produced. The rotational speed of the crankshaft is steady and the engine runs along according to plan. This is on the grounds that the mass of the flywheel applies inertia which kept the motor crankshaft spinning between every piston firing.
5. Weight Manipulation
The heaviness of a flywheel decides the exhibition of an engine. The weight is designed and planned based on the presentation of the vehicles. Heavier flywheels permit the engine to work under loads that make the engine bog down. Large truck or trailer is great with heavier flywheels while sports vehicle and two or three commercial vehicles take full advantage of lighter flywheels.
Working Principle of a Flywheel
The functioning guideline of a flywheel is very simple and interesting as it stores energy for the vehicle’s utilization. Simply the manner in which mechanical battery stores energy in a chemical form, flywheels save the power as motor energy.
More energy is produced as the flywheel turns at a higher speed. This is on the grounds that lighter flywheels produce two times the energy than flywheels that weighs more or double. The lighter the flywheel the more energy is stored. In any case, for heavier vehicles like trailers, trucks, vans, and so on, heavier ones will be a reasonable choice. This is on the grounds that they carry the additional load and are not essential to run at higher velocities.
Thus, knowing how a flywheel work is that the higher the speed the higher the energy stored. In any case, if the speed continued to increase, the wheel material probably won’t have the option to deal with the force. This may lead to breaking up.
How does a Flywheel Works?
The essential working principle or guideline of a flywheel is that it absorbs rotational energy during the power stroke and delivers that energy during different strokes ( Suction, compression, and exhaust).
The Working Method of a Flywheel
- The electric engine empowers the flywheel at the exceptionally initial stage.
- This movement causes the piston to move and consume fuel inside the combustion chamber.
- When the power stroke is activated the flywheel draws power from the power stroke and uses it for the other three strokes.
- Along these lines, it helps in stabilizing the rotational movement of the transmission framework.
What are the Materials used for Making a Flywheel?
Below are the types of materials used for making a flywheel: –
- Cast Iron
- Steel
- GFRP
A) Cast Iron
Traditional flywheels are made of cast irons. The significant benefit of cast iron is that it is not expensive. There is least or no requirement for machining as it can be directly utilized in the wake of casting operation.
They likewise go about as incredible dampers and absorb vibrations. They likewise have a few limitations, for example, they have sudden failure and they additionally offer poor elasticity.
B) Steel
In the present time, flywheels are made of high-strength steel as they offer better elasticity and are corrosion-resistant. They are likewise durable and don’t go through failure very easily. Steels are considered a superior choice when compared to cast iron.
C) GFRP
GFRP represents graphite fiber-reinforced polymer. This is viewed as the most ideal decision for making flywheels for modern-day cars and automobiles. They offer incredible density and rigidity and are ideally suited for making flywheels.
Difference between a Flywheel and a Governor
Many individuals confound among flywheel and governor, however, they are two different things. Below are some differences between them.
- A flywheel is utilized to mitigate cyclic changes in accessible energy but a governor is utilized to change the supply of fuel as per the load.
- The energy stored in the flywheel is kinetic which is 100 percent accessible yet the governor mechanism involves erosion.
- Flywheel isn’t utilized when cyclic fluctuations of energy is small or insignificant. While a governor is vital for all kinds of engines since it restricts the fuel supply as per demand.
- In the event that there is a consistent load, Governor will stay idle however because of cyclic fluctuations in energy accessible, the flywheel will always work.
- Governor has no impact on cyclic fluctuations in energy and the flywheel has no influence on the mean speed of the engine.
- Governor controls the mean speed of the engine and the flywheel controls cyclic vacillations in energy.
Advantages of a Flywheel
- Overall cost of the flywheel is less.
- Flywheels have a more prominent life expectancy.
- By utilizing flywheel, it can give you more prominent storage capacity.
- It requires less support and has a lesser thermal loss.
- Flywheel is safe, reliable, and energy-proficient.
- It is not difficult to operate and requires high energy density.
- It is independent of working temperatures.
Disadvantages of a Flywheel
- The primary drawback of the flywheel is that it requires a lot of space.
- They are very costly to manufacture.
- The building materials are consistently an impediment to it.
What are the Common Problems of Flywheel?
Following are the shortcomings that happen when a flywheel is defective:-
1. Clutch Slipping
This issue happens when the gears automatically change while driving. Because of it, the gear may slip. This happens when power isn’t transferred to the wheels, bringing about a clutch failure.
The slipping clutch will ultimately degrade the flywheel as well. The pressure plate might cause an unexpected grinding sound. Different parts of the flywheel in the clutch assembly will heat up. This will prompt bends and even breaks.
2. Clutch Dragging
In this situation, the clutch won’t deliver completely. This will cause various degrees of gear grinding while switching gears.
Besides, it can completely fail to put the vehicle in first gear when it starts at a standstill. This issue isn’t just made in the flywheel yet in the flywheel or crankshaft assembly bearing or bushing.
3. Clutch Chatter
This occurs when the clutch experiences issue locking in. As the clutch gets, it slips along the flywheel and leaves the flywheel over and again. On release, it seems like a stutter or vibration.
Clutch chattering is much of the time in any gear while starting with a full stop. This shortcoming can be challenging to perceive in light of the fact that there is a defect in the clutch disc, pressure plate, or release bearings. These parts can likewise be broken, deformed, or contaminated with oil.
4. Clutch Pedal Vibration
You might have seen that the clutch pedal or vehicle floor is vibrating when the flywheel is damaged. This is on the grounds that the spring mounts of the flywheel have declined. Allow us to let you know that the spring mechanism lessens the vibration brought about by the clutch being utilized.
5. Burning Smell
At the point when the clutch turns bad, a burning smell will produce. This is caused by a faulty flywheel or an unskilled administrator.
The face of the clutch is designed with materials proposed to diminish how much sound the grip makes while working. This produces an excessive amount of intensity because of friction while the confronting isn’t properly operated.
Conclusion
In a manual transmission, the flywheel is a thick metal plate. It’s normally made of cast iron, steel, or, at times, aluminum. It’s very unbending to forestall flexing or war-page during use. The flywheel is a significant part of the engine. Flywheel empowers an engine to run as expected with no adjustment of the rotational motion of the transmission system. Without a flywheel, the engine loses part of the speed that proceeds with the crankshaft speed, so it is needed. Large numbers of motor-driven generators use flywheels for storing energy. They are likewise utilized in satellites for direction control.
In the present time, Modern-day locomotive propulsion frameworks additionally use flywheels. Common uses of a flywheel incorporate smoothing a power yield in reciprocating engines, energy storage, delivering energy at higher rates than the source, controlling the direction of a mechanical framework utilizing a whirligig and response wheel, etc. In vehicle engines, the flywheel smooths out the pulses of energy given by the combustion in the cylinders and to give energy for the compression stroke of the pistons.
Content Source: – explainthatstuff