34 Parts of Motorcycle and Their Function [with Pictures & Names]
![34 Parts of Motorcycle and Their Function [with Pictures & Names]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Parts-of-Motorcycle-1024x539.jpg)
Parts of Motorcycle – [with Pictures & Names]: – Motorcycles or Cruisers, frequently called a motorbike, bicycles, cycles, or on the other hand (if three-wheeled) motorcycles, is a two or three-wheeled engine vehicles. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of various purposes. You might live for riding your cruiser, yet just haven simple information on its parts. While you needn’t bother with to be an expert technician, you still in any case know a little about the parts so you can make smart choices while replacing them.
Motorcycles are however intriguing as they may be invigorating. It can assist you with riding your bike securely and you can likewise capitalize on what your vehicle can do.
A few specialized technologies might appear to be a bit intimidating for inexperienced riders. Individuals who are new to the world of bikes might struggle to comprehend how a motorcycle works.
Basic Parts of Motorcycle
1. Engine: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

The engine is a lot of the pulsating heart of any motorcycle. From a Yamaha racer to a scooter, each motorcycle depends on an internal combustion engine for power.
This is a small, encased chamber wherein spark plugs ignite a controlled combination of air and fuel. The ignited fuel quickly expands within its cylinder. The pressure created then controls a cylinder. This piston, associated with a rod (or con-rod), spins an enormous axle called a crank, which then, at that point, powers the rear wheel.
This crank develop the force. Then the crank pushes the piston back into the cylinder, removing with it all the consumed gas. The gas then, at that point, leaves the engine through two valves that lead to the fumes or exhaust.
2. Carburetor: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

A Bike carburetor is an indispensable part of a bike engine since it controls the ratio of the fuel and air mixture going inside the engine which is liable for its movement. Since the cost or expense of fuel injector innovation is more than carburetors, the majority of the bikes in most countries actually utilize carburetors.
3. Suspension: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

The Primary aim of bike suspension is to keep your wheels firmly on the ground. Without a front and back suspension framework in place, your bike would lose footing at the slightest bump. Motorbike suspension utilizes a combination of a spring and a dampener. These ingest the impact and separate the chassis of the bike from the rider.
Each bike has front forks suspension and a back suspension, which is generally either a swing arm or pressure-driven dampener at the rear wheel.
4. Exhaust: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

The exhaust is one of the most critical parts of a motorcycle that keep your bike running along smoothly. At the point when the fuel burns out within the internal combustion chambers, the exhaust channels it out.
An exhaust is likewise essential for keeping the engine’s noise at a reasonable volume. Without an exhaust and the suppressor inside, your bike would make a flat-out the racket.
5. Wheels: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
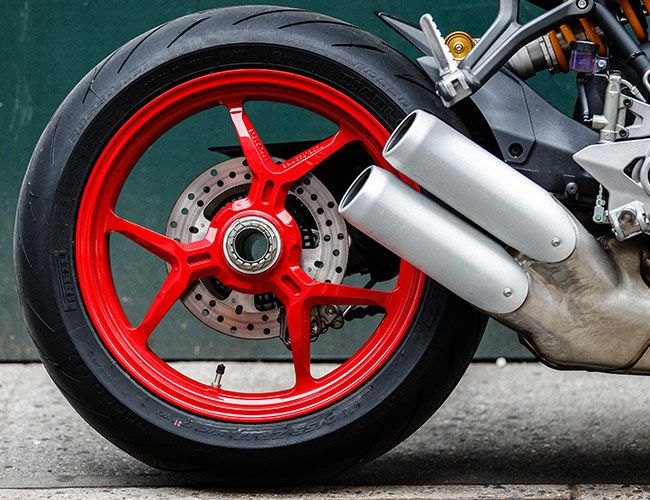

Wheels are the motorcycle parts that get power from the engine. A fundamental part of a wheel is a rubber tire. Motorcycle tires come in different shapes and sizes to suit every vehicle or the rider’s style. ( Types of Tyres )
For the most part, Tyre’s can be divided into three types: –
a) Off-Road Tyre’s
These tires have an exceptionally rough and protuberant shape. The aim of the structure is to spread loose dirt and shape to the lopsided ground to allow traction.
b) Road or Street Tires
Street tires are for the most part in every case flat and smooth. Their aim is to keep however much of the bike’s wheel on the ground as could reasonably be expected to accomplish the best traction.
c) Dual Sports Tires
These are a hybrid of the two types referenced above. They actually retain the roughness of the off-road tires. Be that as it may, they are more extensive and complement, making them reasonable for any terrain type.
6. Brakes: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
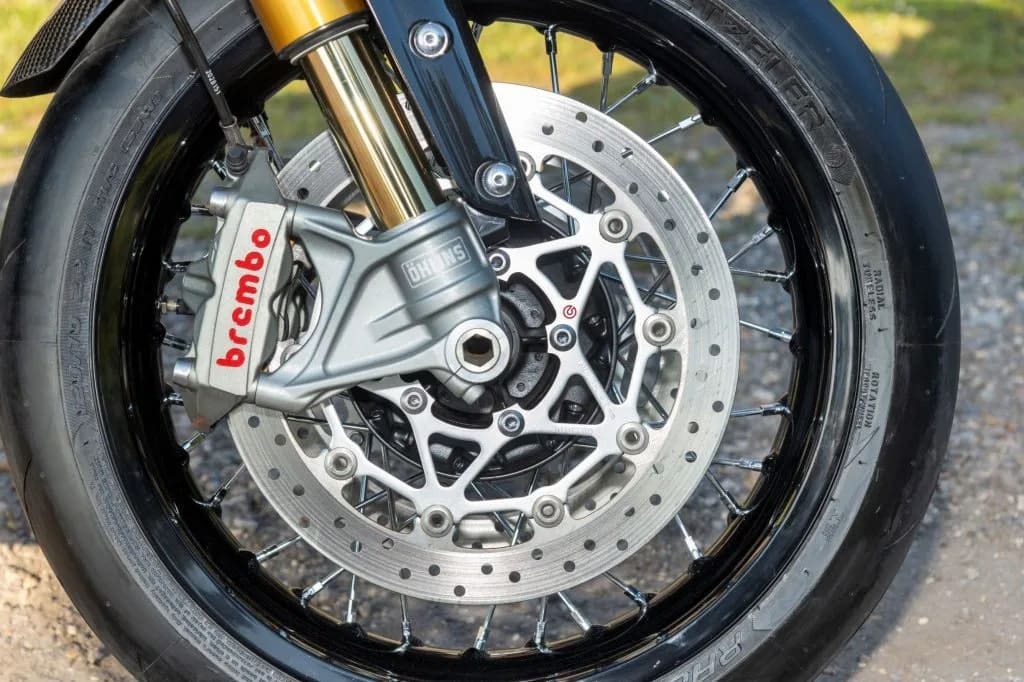

Brakes are parts of a bike that you couldn’t do or manage without. Assuming that you comprehend how your brakes work, you can ride more securely and save money on the maintenance expenses of replacing them.
Bikes have two distinct sets of brakes to control the front and back wheels. The front wheel requires significantly more braking power, so it is generally more prominent than the rear brake.
There are two types of motorcycle brakes that you’re probably going to find – Disc brakes and drum brakes.
- Disc brakes are quite common on larger motorcycles as the disc generates an extensively more braking power.
- Drum brakes are a more seasoned type, for the most part, found on more modest motorcycles or utilized principally as a back brake.
7. Exhaust Pipe: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
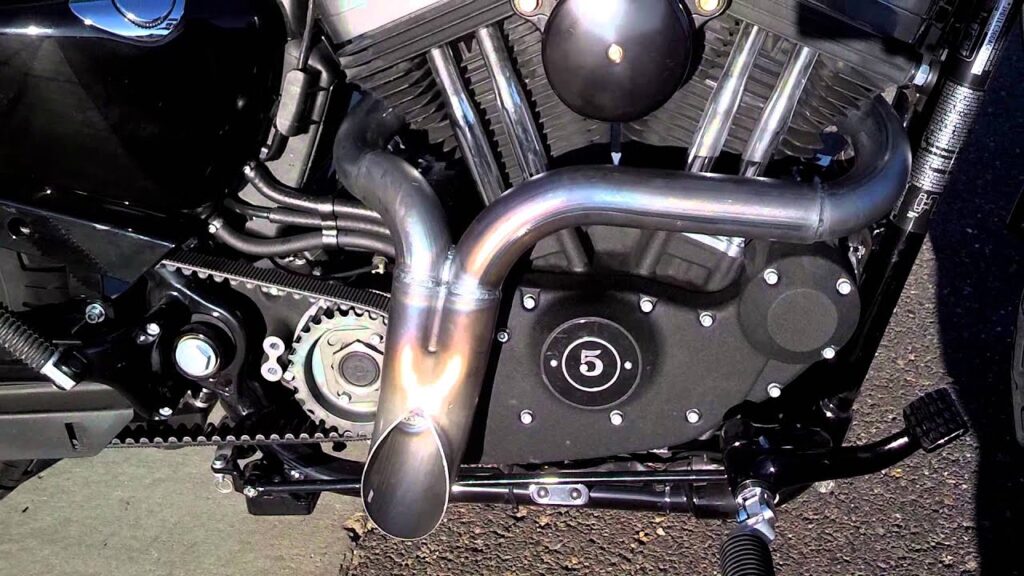

Exhaust or Fumes gases are collected from the cylindrical head in the motor by an exhaust system. The exhaust system goes about as a funnel, redirecting exhaust gases from all cylinders of the engine and then, at that point, releases them through a solitary opening, frequently alluded to as the front pipe.
8. Ignition Circuit Breaker: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
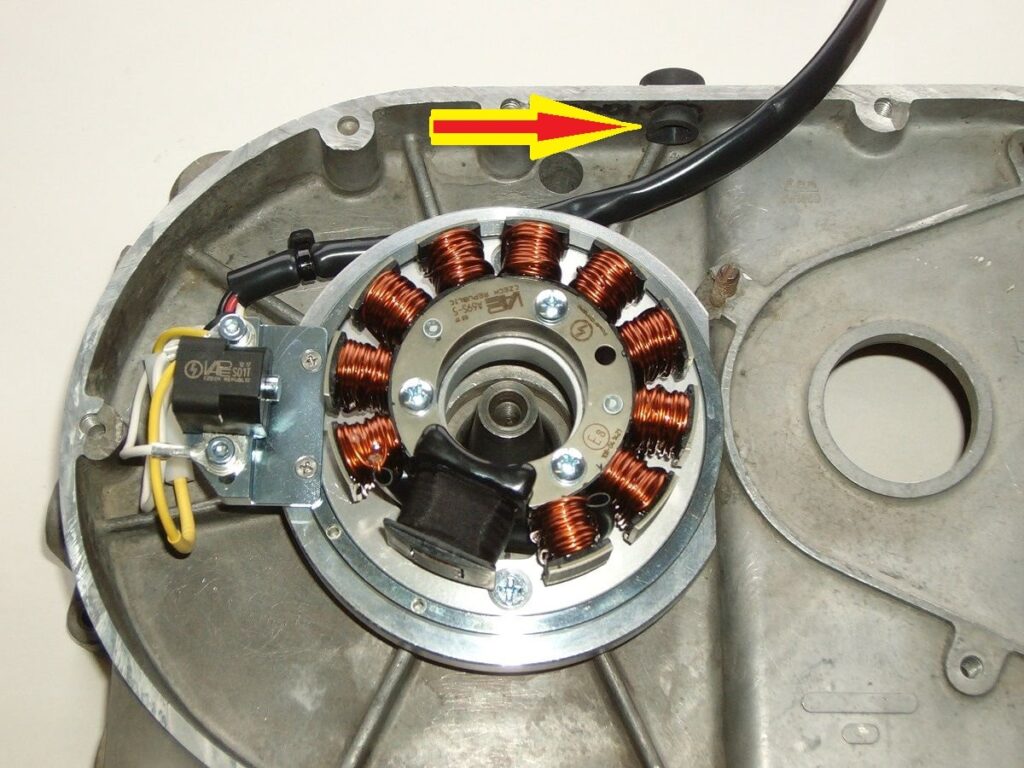

As the engine pivots, the distributor shaft cam turns until the high point on the cam causes the breaker point to out of nowhere suddenly. Quickly, when the points open current flow stops through the primary or essential windings of the ignition coil. This makes the magnetic field collapse around the coil.
9. Gas Tank: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
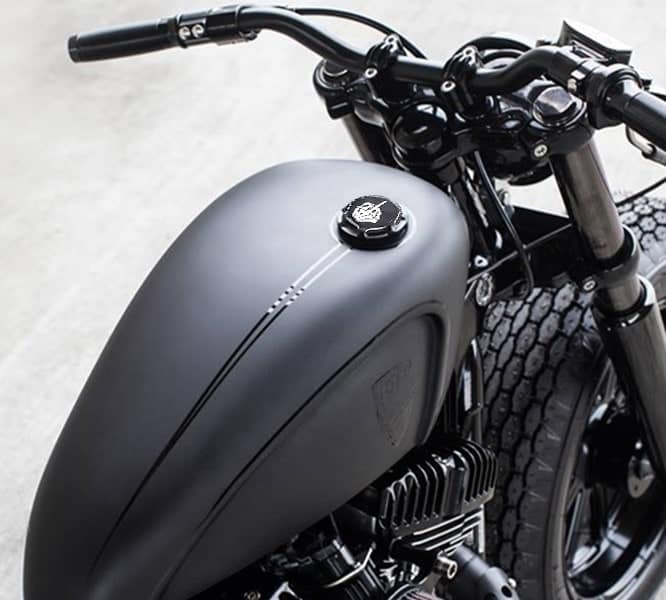

The white region over the blue, inside the tank, is the “normal” fuel and is what the longer tube can reach. Each tube has an opening toward the end, keeping it from reaching the fuel which is lower than its upper end. There is no separate or different reserve tank. Practically all bikes have only one gas tank.
10. Mufflers: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
The muffler contains tubes, channels, and openings that direct gases and reduce exhaust pressure. It calms the motor by decreasing the sound tension discharged. The suppressor is planned not to simply hose sound, yet to consolidate sound waves and make them counterbalance each other.
11. Oil Tank: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

A bike oil tank is a tank that holds the limit of oil used to cool the cruiser. Motorcycles that utilize oil to keep the engine cool have an oil tank taking into account excess oil to circulate through the engine and through an oil cooler mounted to the front of the bike.
12. Rear Wheel Shock Absorber: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

At the point when a motorcycle experiences a bump, dampers slow spring pressure and rebound as the liquid gradually goes through the passages inside the shock body. kinetic energy from spring movement transforms into heat energy inside the damper, and the pressure-driven fluid scatters the heat.
13. Seat: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
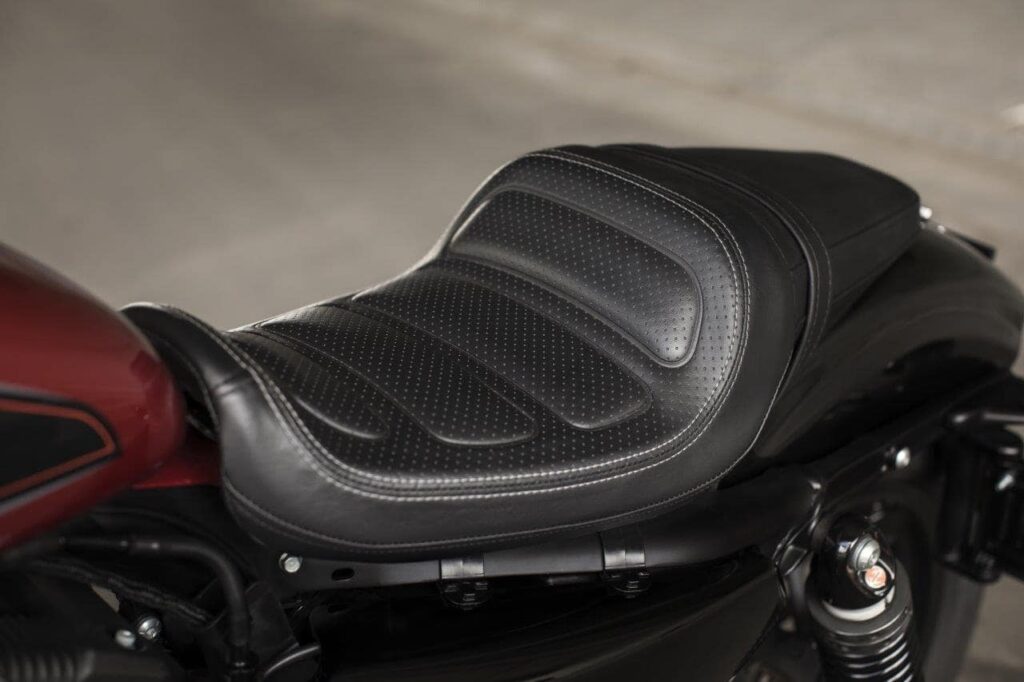

The shape and size of a motorcycle seat vary contingent upon the type of bike you have. Seats are one of the most widely recognized motorcycle parts that a rider might want to change. Contingent upon your preference, you should add padding or cushioning or a backrest, particularly for long excursions. A few motorcycles likewise have an additional seat space for a traveler or pillion.
14. Dashboard: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
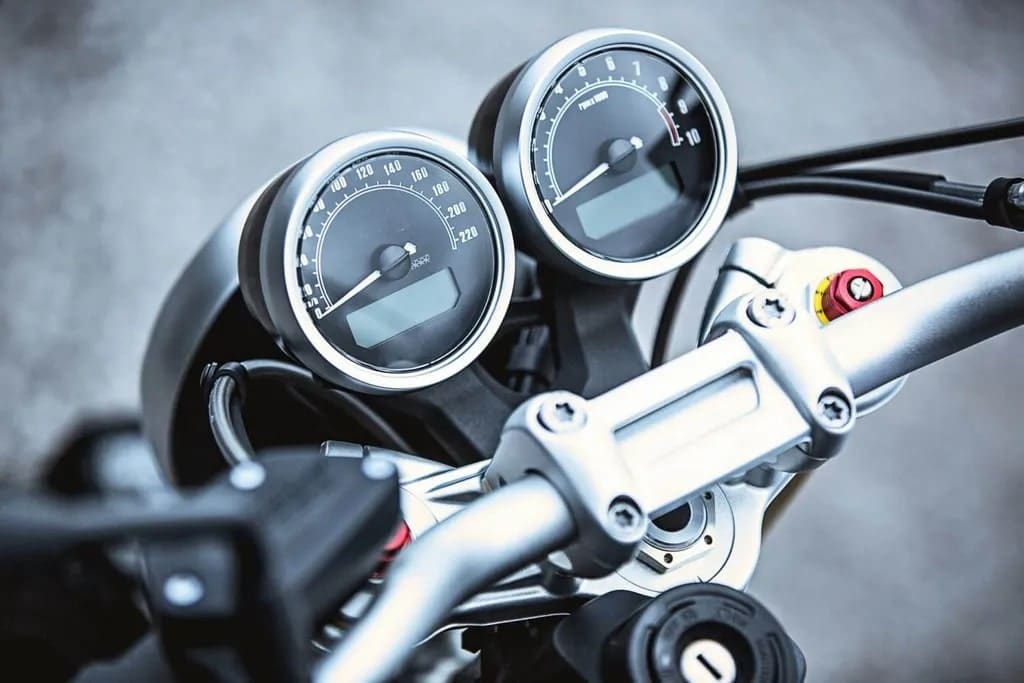

Modern-day motorcycle dashboards are one more fundamental part of a bike. The positioning and configuration of a dashboard vary among models and their makers. Yet, it is constantly located between or beneath the handlebars in clear view for the driver.
A motorcycle dashboard will quite often incorporate the following things:
- Tachometer – This tells the rider their ongoing RPM (Revolutions each minute) value.
- Speedometer – A speedometer tells the driver about the speed of the motorcycle (in MPH or KM).
15. Handlebars: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

Different parts of a bike that you’ll need to get to grips with are the handlebars. The handlebars of a motorcycle or cruiser control the steering and the direction that the bike is going. Handlebars come in many styles and sizes to suit various rider’s preferences.
As well as direction and steering, the handlebars on a cruiser likewise incorporate the accompanying control parts:
- Engine cut-off switch
- Electrical start-up switch
- A controller for the motorcycle lights
- Front brake control handle
16. Mirror: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
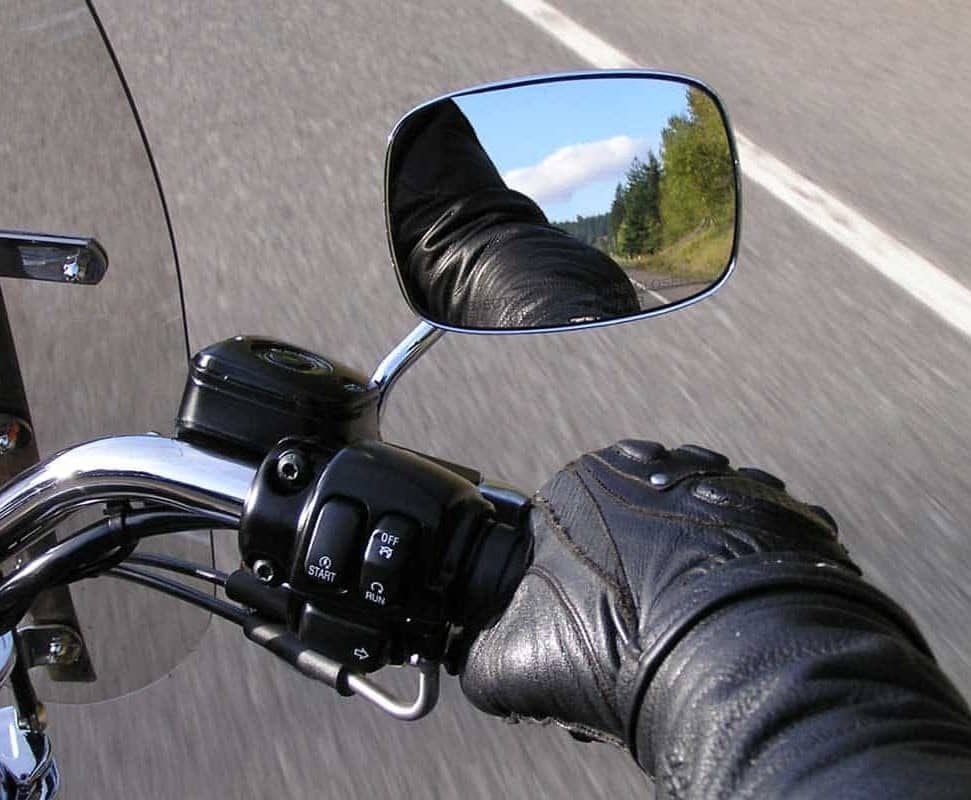

One more significant part of a motorcycle is its Mirror. Mostly convex mirror are utilized in Bikes. The convex mirror produces an upright image of any object and offers a wide viewing area or region when contrasted with the plane mirror. offers a wide viewing area as compared to the plane mirror.
17. Throttle: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
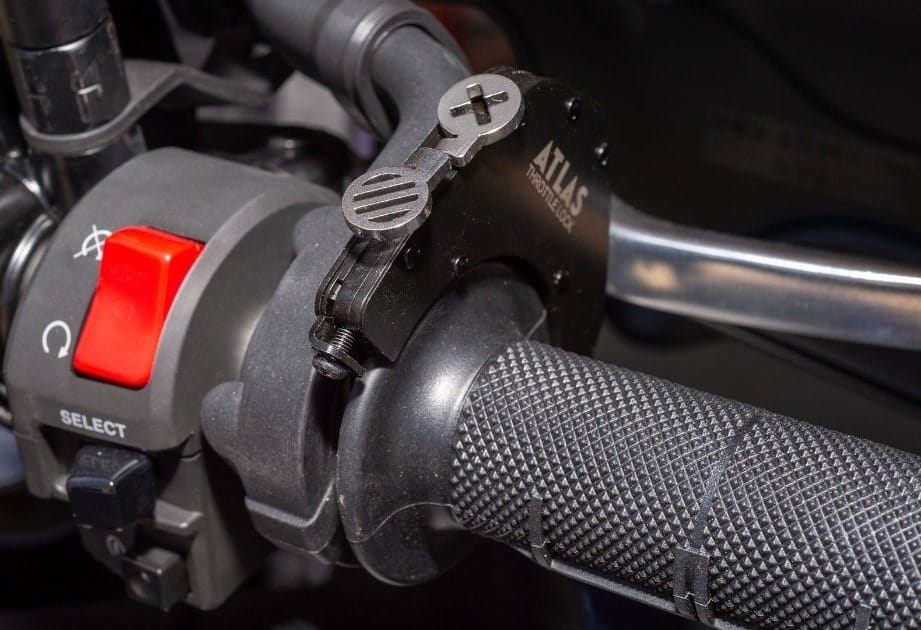

At the point when you are in the driver’s seat of a motorcycle, you really want to understand what you’re doing. unlike the name suggests, you ought to just at any point have a light grip on your bike’s throttle. Expecting you to handle the throttle switch excessively, it could make the bike jolt forward with great power and effectiveness.
The purpose of the throttle is to increase or reduce the speed of the bike, contingent upon the direction that you turn the lever.
18. Battery: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
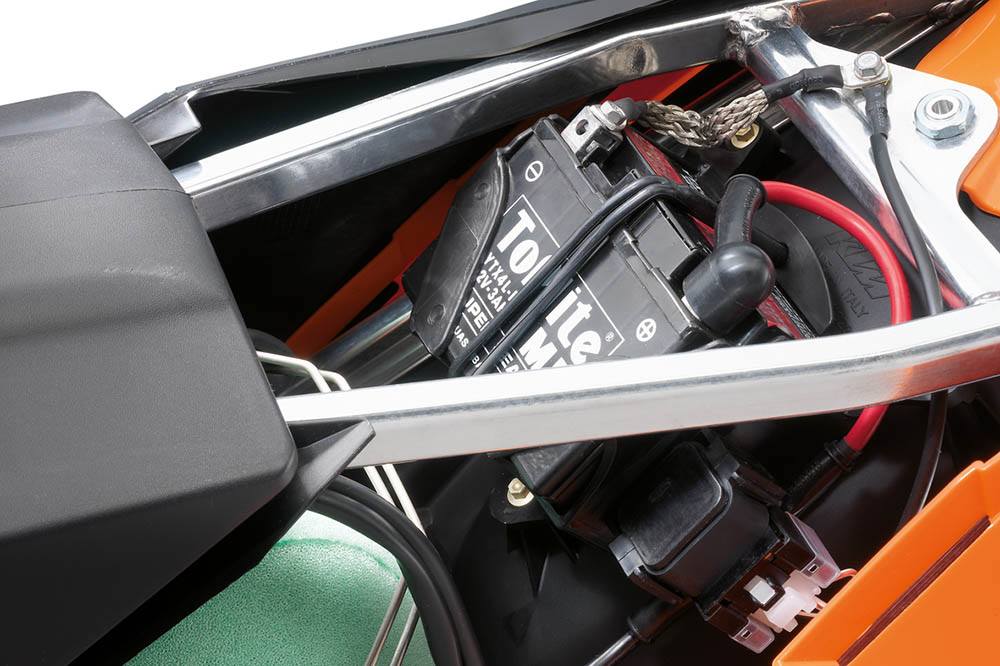

One more significant part of a cruiser is its battery. There is life expectancy of batteries . A conventional corrosive filled battery has a life span of two to five years. On the off chance that you suspect now is the ideal time to replace your bike battery,you can counsel a close by service center.
19. Clutch Lever: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
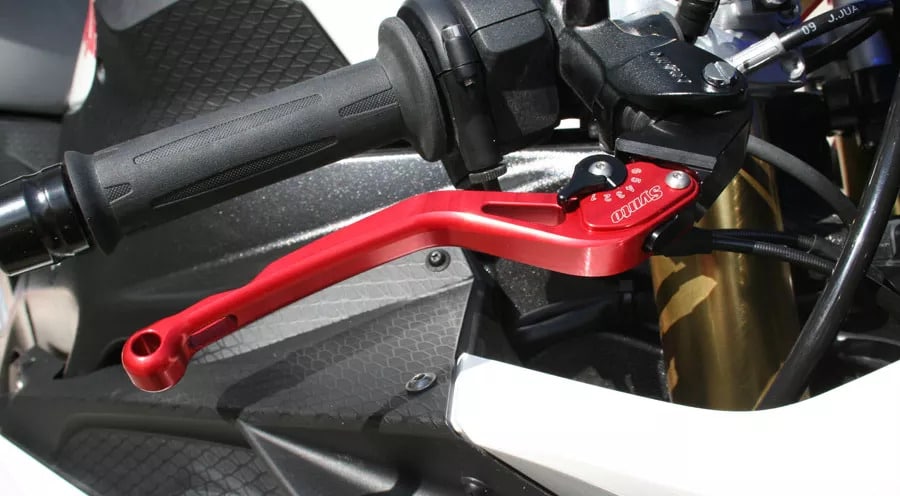

The Clutch lever is one of the most indispensable bike parts. A motorcycle’s clutch is located adjacent to the brake lever on the right-hand side of a bike.
To utilize the clutch on a bike, pull the lever towards you to dispense your engine’s power to the rear wheel. You can then switch gears. Once complete, release the lever or switch to return capacity to the back wheel.
It is fundamental that you comprehend how your clutch functions. Poor clutch control can bring about slowing down your motorcycle while slowing down or switching gears.
20. Brake Levers: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
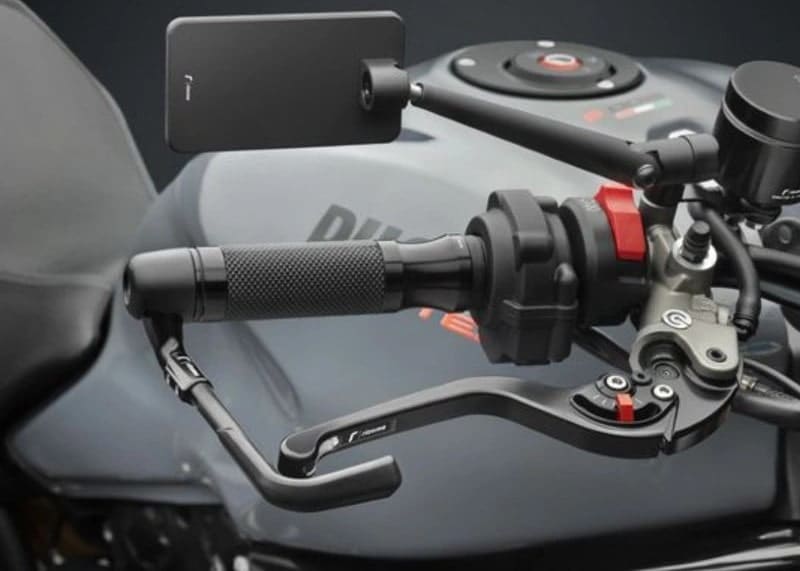

Unlike a bicycle, there is just a single brake lever on the motorcycle. The front left lever controls the front brakes, the rear brake is controlled by a pedal. To operate the front brake lever of a bike effectively, utilize all four fingers to squeeze it towards you. The stronger you pull the brake, the quicker the biker will come to halt.
21. Brake Cable: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
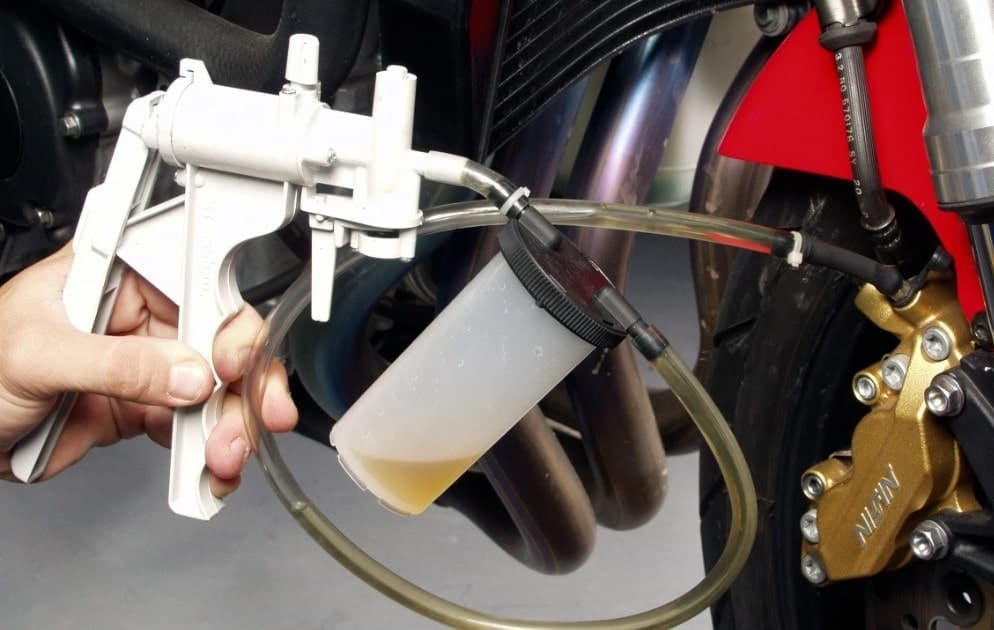

A cable or a lever draws in the master cylinder, making a piston apply pressure on the brake fluid. Since brake fluid can’t be compressed, that pressure is passed on through the brake lines to one more piston in the brake caliper.
22. Horn: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

Pressing or Squeezing the horn button on the handlebar initiates the electromagnet, which pulls on the diaphragm until a bunch of contact points touch, breaking the electromagnet’s pull on the steel and returning the diaphragm to its unique process to begin the bike once more.
23. Gear Changer: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

To change or switch gears on a motorcycle, you’ll have to utilize both the clutch handle and a foot pedal on the left side of the bike. Controlling the clutch on a bike is like a clutch in a car. At the point when you pull in the clutch lever, you can be as firm or fast. Nonetheless, when you reconnect the clutch by releasing pressure, you must do as such in a smooth and controlled manner to prevent it from slowing down.
24. Spark Advance: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
Spark advance implies that the spark plugs are firing prior to the compression stroke, farther from TDC. The air and fuel blend in the ignition chamber doesn’t burn immediately. Ignition timing advancing may be expected to permit time to get everything ignited.
25. Ignition Switch: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
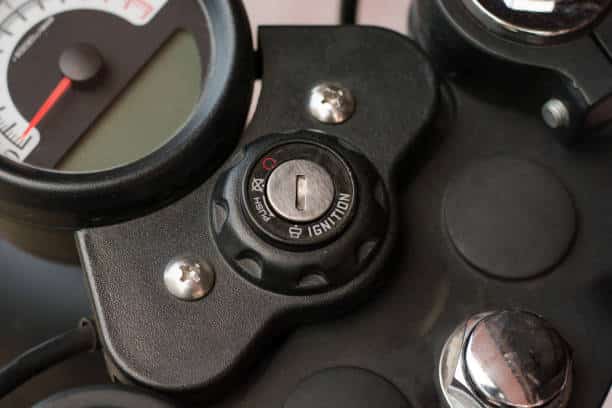

An ignition switch, or starter switch, is the leading switch that administers the power in the main electrical of a motorcycle. When the ignition switch is incited by the key or the press of a button, it initiates the voltage from the battery to the ignition coil to produce an engine spark. The engine spark from the coil or curls is directed to the spark plugs to ignite the fuel to make the vehicle run.
26. Balloon Tires: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
A Balloon tire is a sort of wide, large-volume, low-pressure tire. Balloon tires have a bigger surface contrasted with any traditional tires. Moreover, the low PSI permits the wheels to move on a superficial level easily when they squat, or flatten out to keep from soaking in delicate, sugar like sand. The low air pressure likewise makes the tires durable over various terrains.
27. Fender: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
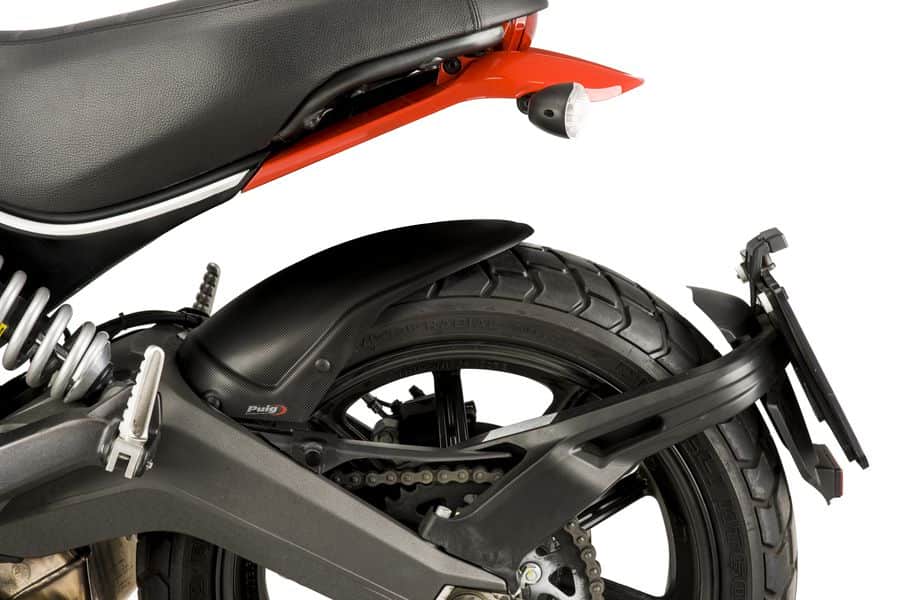

A fender is basically a covering for your bike tires that safeguards you from the rain. Riding with fenders will keep the rain from sprinkling a streak of muddy water up your back, over your shoes, and all over your face.
28. Foot Pegs: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
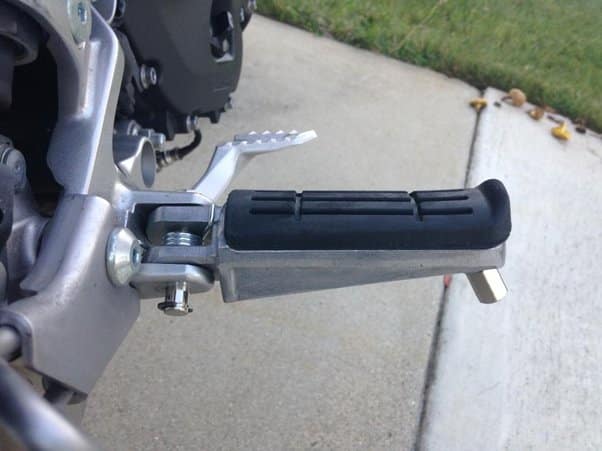

There are three principal foot-control parts of a bike that you’ll have to master. There are the rear brake pedal, the gear shifting or moving pedal, and the kickstart pedal. The rear brake pedal is on the right-hand side of the motorcycle or cruiser, for the most part over the footrest. To utilize this brake, you should utilize your foot to apply pressure until the bike slows.
A bike’s gear pedal is usually located on the left-hand side, close to the footrest. At the point when you need to shift or change gears, utilize both the clutch handle and the gear pedal as one.
At long last, the Kick start pedal is additionally on the right side of the motorcycle, next to the footrest. The motivation behind the kick start pedal is to ignite the spark plugs and prepare the bike for some action.
29. Side Stand: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
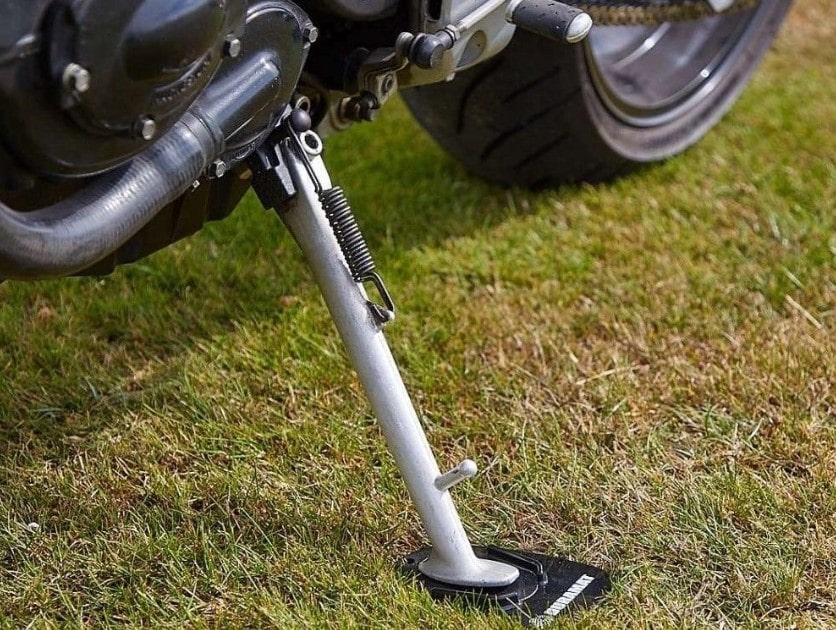

It is utilized for travelling out from one place then onto the next place. So it is exceptionally valuable and furthermore responsible for causes of some minor and significant mishap on account of forgetting to lift off the side stand. Side stand plays a vital part while the vehicle is in the rest position.
30. Headlights: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
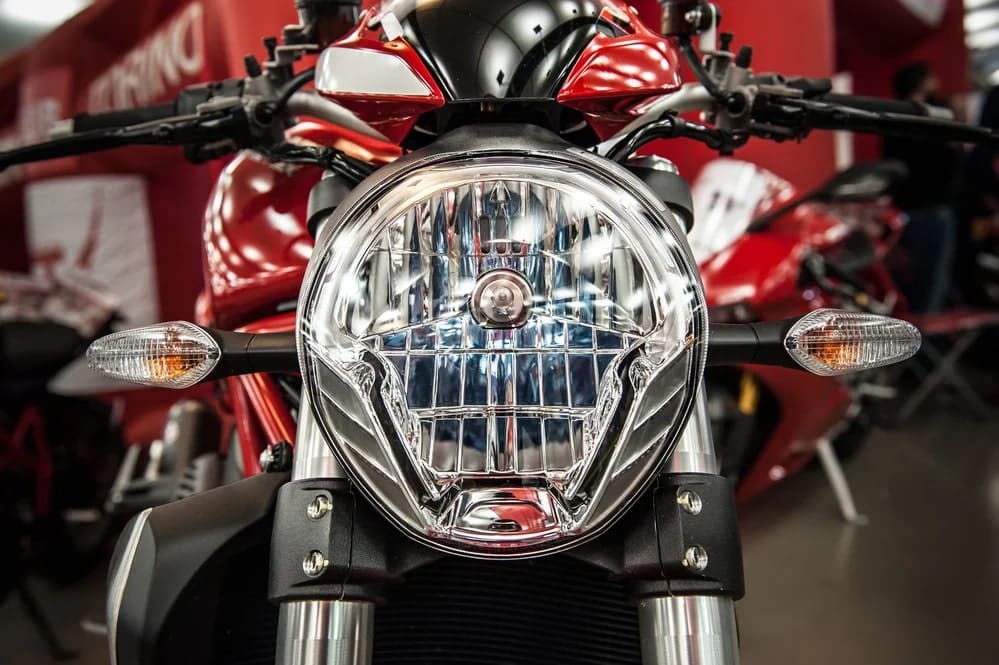

These headlamps are special purpose housing with a focal point in them. There are reflectors in it too, yet the light is totally captured by the lens which gives direction to the light flow. Running daytime headlights is a safety strategy that has been used by motorcycles for a really long time to make themselves more noticeable to different vehicles.
31. Tail and Stop Light: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
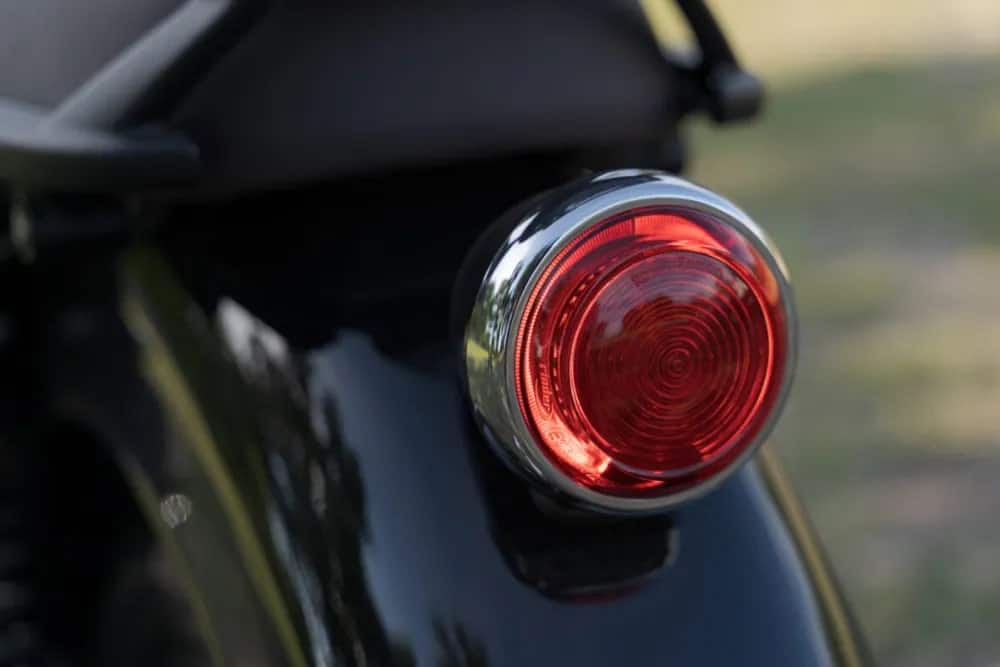

With a tail light, a bike makes its presence noticeable to other vehicles behind it while the brake light warns the driver behind to be careful of easing back the vehicle. As a general rule, on applying brakes brightness of the tail light increases. The vast majority of modern-day vehicles accomplish this with various bulbs for tail lights and brake lights in the same housing. Be that as it may, this isn’t correct if there should be an occurrence of bicycles because of restricted housing space.
32. Signal Lights: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
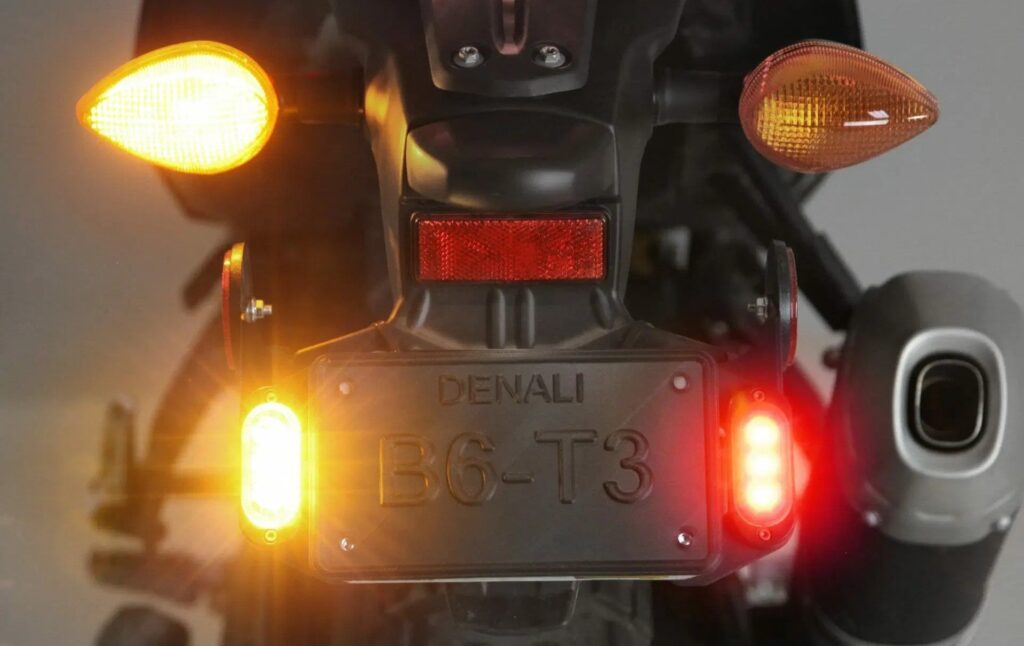

Understanding the role of signal lights on your dashboard is critical to keeping or guarding your safety on the road. To make things more easier or straightforward for riders, most signal lights on a bike are symbols. They are likewise color-coded to indicate how serious they are – from green to red.
The red and golden warning lights (which show the usefulness of the more serious parts of a bike) are mentioned below: –
a) Bike Ignition Light
This light displays as a battery symbol. It ought to possibly illuminate when the ignition is turned on. Furthermore, it automatically switches itself off after a few moments.
b) Oil Pressure Light
The oil pressure warning light seems to be like an oil container symbol. Assuming it enlightens while riding, it lets the driver know that their oil pressure is low.
c) ABS Light
Not all bikes will have ABS (anti-locking braking mechanism). However, on the off chance that yours does and the ‘ABS’ light is illuminated, it could be an indication of an issue with your brakes.
d) Engine or Motor Temperature Light
This warning light indicates low engine coolant levels. It warns or cautions you that the engine may overheat. You ought to stop and switch your engine off quickly if this light comes on.
33. Number Plate: ( Parts of Motorcycle )

A number plate, otherwise called an registration plate or a license plate, is just a metal board representation of that unique registration ID. It is attached to the motorbike and has the authority registration ID emblazoned on it. Number plates are set at the front and the rear of a motorbike and assists with identifying it.
34. Storage Space: ( Parts of Motorcycle )
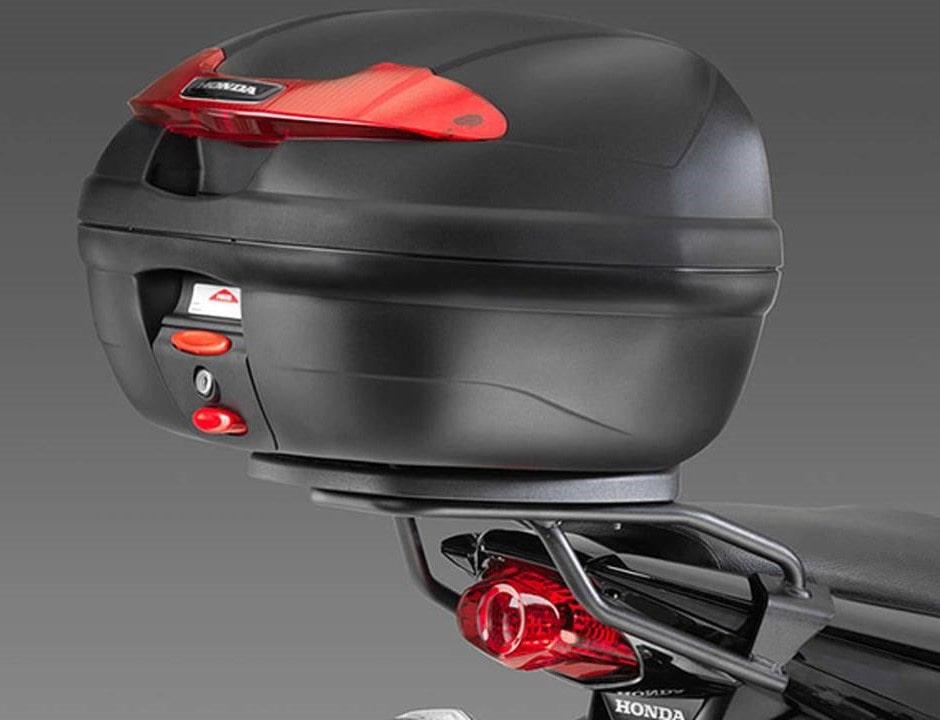

Not all bicycles will have an in-built extra or storage space. Nonetheless, extra storage is one of the most notable and supportive motorcycle accessories. The most popular storage parts for bikes are known as a ‘top box’ or hardtail bag. These are strong framed storage boxes that are connected to the tail end of the bike.
- Saddlebags: A bunch of bags that mount or drape on the back bumper or seat to take into consideration the storage.
- Rear or Back Carrier Bag: This kind of storage can be either a bag or box that can be mounted or strapped down to a rear seat or mounting point on the bike.
- Rack: Usually an add-on mounting point behind the rear or back seat or that replaces the rear seat for discretionary mounting points for bags or luggage.
- Tank Bag: This is a bag that either has straps or magnets that mount to the fuel tank to give you storage options.
- Backpack: Most individuals simply getting a bike utilizes a backpack or rucksack to bring items with them on rides. Assuming that you utilize a Backpack, try and utilize one that doesn’t move much while riding or one explicitly designed for bike riders.
Conclusion
Riding motorcycles or cruisers can be fun and it can be amusing to learn much more about them as well. Thus, we will investigate a portion of the things you may not be aware of cruisers but rather you might have for a long time truly needed to know. It is vital to know the parts of the vehicle you are driving and knowing how they work or function will help you in the future during any emergency.