Types of Ladders – Introduction, Uses, Material & Safety Tips [Complete Details]
![Types of Ladders - Introduction, Uses, Material & Safety Tips [Complete Details]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Ladders-1024x539.jpg)
Introduction
Types of Ladders – Introduction, Uses, Material & Safety Tips [Complete Details] :- It is really critical to select the right ladder which can be quite relevant in easing down your job. It is even more important than the tallness as it likewise manages the accommodation, security, sturdiness and application.
Even if you are a mortgage holder or an entrepreneur, it may not be reasonable to possess and store a few distinct sorts of stepping stools without a moment’s delay. How might you make the most out of your stepping stool speculation while as yet keeping up with well being and accommodation? Investigate the accompanying stepping stool types, grades and materials to observe an answer that will work for your necessities.
Types of Ladders
Consider which sort of ladder will work best for your projects before you begin. There are numerous types of ladder with different configurations available. Each of them has its own set of features that are found helping you in order to improve your workflow. Here are a few different sorts of ladders to think about.
1. Step Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )
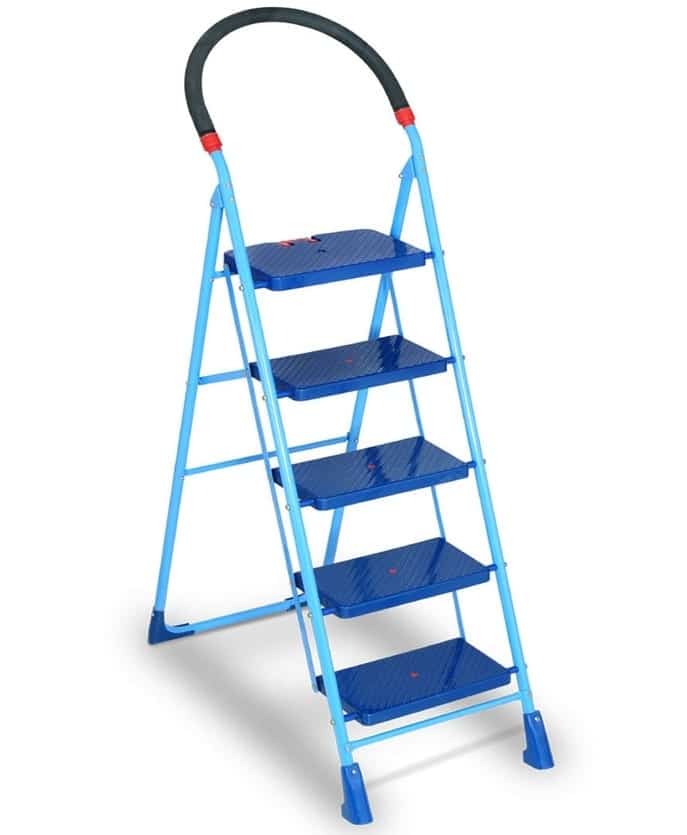

A stepladder is referred to as one of the most common ladder types with mostly universal application. These are the ones which are found featuring an upside-down V-shaped self-supporting structure. This clearly depicts that one doesn’t have to prop it against a wall or any other structure in order to use it. Stepladders are quite flexible and can also fold together for easy transportation.
The following are some of the most common properties of a stepladder:
- Height: The height of this ladder is fixed within 4 to 20 feet.
- Structure: An upside-down “V” shape that expands and is hinged for simple storage.
- Sides: Two sides structure whereas only one is found to be climbable.
- Only one person can be accommodated.
- Ground support: The bottom of the ladder requires a flat establishing support.
One advantage of a stepladder’s plan is that you can set it up anyplace with level ground. This adaptable ability makes it one of the most outstanding multi-use stepping stools accessible. The stepladder which is provides is for the right tallness to your task, it very well might be a decent decision for painting, changing lights, adorning, development, arranging and there is no limit to this.
2. Straight Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )

Straight ladders, also known as single ladders, resemble one half of a stepladder. Straight ladders require some type of anchor at their uppermost portion because they are not self-supporting. Straight ladders are known to be quite portable but on the other hand they are found lacking hinges that easily allow them to take less room whenever not in use.
The following are some of the most common properties of a straight ladder:
- Height: The length is non-adjustable and runs from 4 to 30 feet.
- Design of the structure: Two side rails are connected by rungs that are evenly spaced.
- Sides: It has only one side through which it can be climbed.
- Only one person can be accommodated.
- Ground support: Both supports of flat ground is mandatory.
3. Platform Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )
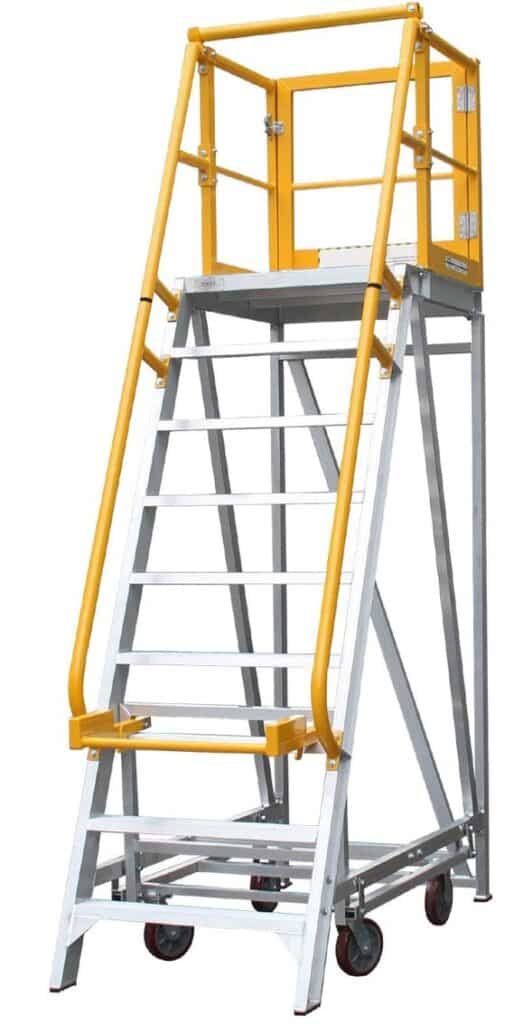

The platform at the top of the ladder usually has a railing on three sides, with the side closest to the rungs being open. The design of a platform ladder allows you to stand at its highest point, which is often not possible with other ladder types.
Normal qualities of a stage stepping stool include:
- Stature: Non-movable length goes from 2 feet to 18 feet
- Foundational layout: Accompanies a stage along with railings that is pivoted for simple capacity
- Sides: Two-sided, however just a single side is climbable
- Limit: One individual in particular
- Ground support: Requires level ground support for each of the four feet
These ladders are ideal for projects that require you to stand safely on a ladder for extended periods of time. Landscaping, painting, placing hardware in high locations, arranging displays, and constructing are just a few examples of these projects.
4. Extension Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )

Similar as straight stepping stools, augmentation stepping stools are non-self-supporting stepping stools with one side. Expansion stepping stools utilize a few areas on directed tracks to give extra length depending on the situation. Many stepping stools highlight rope and pulley frameworks that join to the customizable segments to support expansion.
The following are some of the most common features of an extension ladder:
- Height: The height of a both section ladder seems to be adjusting from height varying 32 to 60 feet. The length of a three-section ladder can be adjusted from 60 to 72 feet.
- Design of the structure: Two or three adjustable sections, as well as two or three side rails connected with regularly spaced rungs
- Sides: There is only one side that can be adjusted.
- Only one person can be accommodated.
- Ground support: Two feet of flat ground support is required.
The capacity to change expansion stepping stools settles on them a flexible decision for occupations where you want to arrive at tall statures and have close admittance to the task point. Almost a quarter of these activities are found incorporating various types of material, development along with various occupations.
5. Trestle Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )
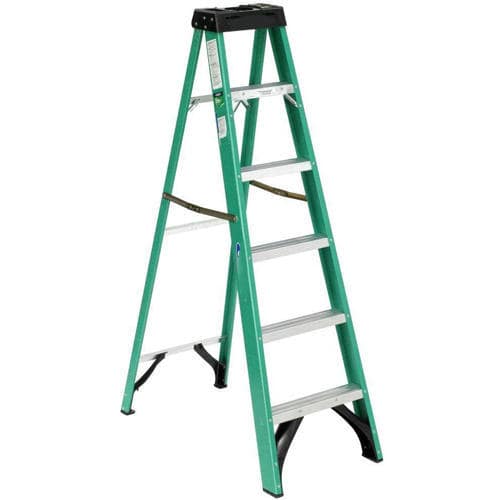

Otherwise called twofold front stepping stools, beam stepping stools are intended to do what most stepping stools can’t – support two individuals without a moment’s delay.
Basic requirements of a brace stepping stool are as follows:
- Stature: Static with a specific length up to 20 feet
- Foundational layout: Hinged for simple capacity
- Sides: Two climbable sides
- Limit: Only two individuals on the double at a time
- Ground support: Min. requirement of level ground support of around 4 feets
6. Multi-Way Ladders: ( Types of Ladders )
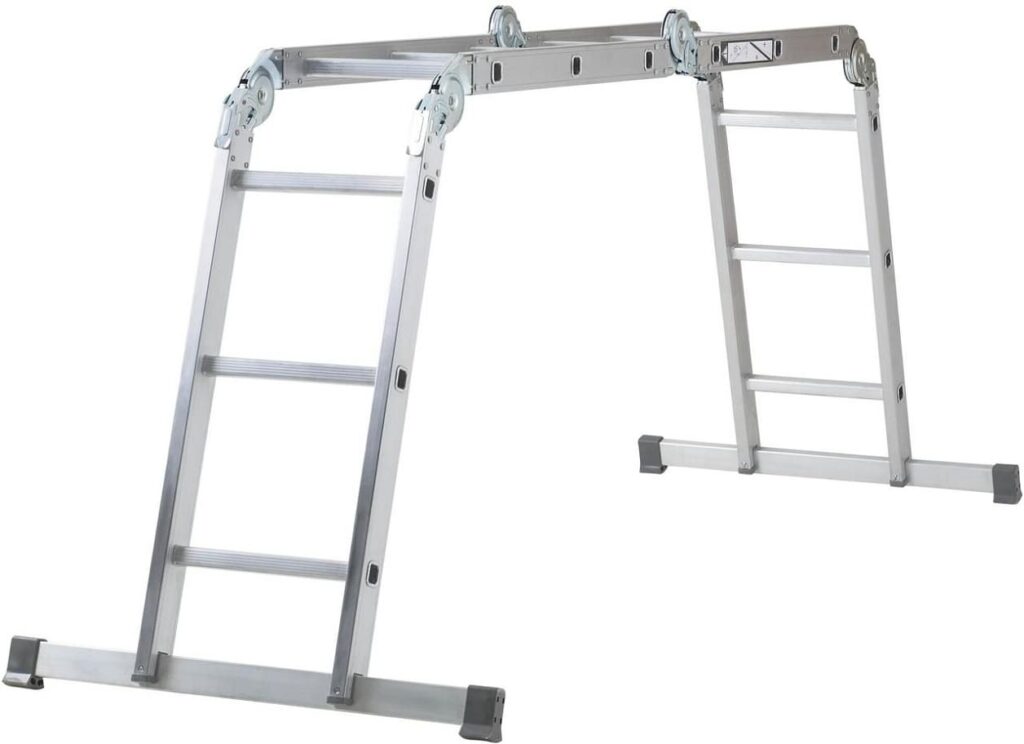

Multi-way stepping stools regularly fuse more than one stepping stool type into a solitary, changeable stepping stool. These stepping stools generally come as two-sided self-supporting constructions with the capacity to work as a stepladder, expansion stepping stool, beam stepping stool and that’s just the beginning. The particular producer and item will figure out what sort of abilities a multi-way stepping stool has
A multi-way ladder has the following characteristics:
- Height: Adjustable length between 4 and 13 feet.
- Transformable structure with hinges for convenient storage is the structural design.
- Sides: Most are two-sided.
- Suitable for one to two persons
- Ground support: The bottom of the ladder requires a flat support.
Situations that might warrant multi-way stepping stools incorporate home redesigns, private venture support needs, different inside or outside cleaning activities and then some.
Material of Ladders
Ladders are found being made up of various types of material that are found having their own set of advantages as well as disadvantages. Ladders are most commonly found being built of materials like metal, wood, or fiberglass.
A) Metal
Most metal stepping stools are produced using aluminum, which offers key benefits and impediments.
The aces of Aluminum Stepping Stools include
- Lightweight: Aluminum material keeps stepping stools light and simple to ship. This can save time and energy on projects that require incessant stepping stool repositioning.
- Reasonable: Compared to different materials, aluminum is economical. This can assist you with saving costs while purchasing different stepping stools.
- Long-lasting: Aluminum is corrosion-resistant and will not deteriorate in extreme weather. This is one of the best option if you are looking to get the most out of your ladder.
The cons of Aluminum Ladders include
- Conducts electricity: An aluminum stepping stool can finish an electrical circuit between an electrical source, the stepping stool and your body. Assuming you’re chipping away at an electrical undertaking, aluminum stepping stools might cause stuns that could prompt falls and genuine wounds in the event that you interact with a live wire while remaining on one. In the event that your tasks regularly include power, an aluminum stepping stool may not be the most ideal decision.
- Reflects ambient temperature: When you utilise an aluminum ladder in direct sunlight or in extreme cold, the metal will reflect the temperature of your surroundings.
B) Wood
The Pros of Wooden Ladders include
- Non-conductive: Wooden stepping stools don’t direct power, which settles on them a protected decision for electrical ventures.
- Reasonable: Like aluminum, wooden stepping stools are somewhat economical. This can assist you with saving costs while purchasing different stepping stools.
- Impervious to encompassing temperature: Wooden stepping stools will not become as warm or cold to the touch in outrageous atmospheric conditions.
The Cons of Wooden Ladders include
- Heavier Wooden Ladders: A wooden ladder can become difficult if you’re working on a job that requires frequent ladder relocation.
- Issues with long-term durability: It is a time taking process especially outside in the rain, snow, or excessive heat can cause wooden ladders to decay. If you plan to store your ladder outside or connect it to the outside of your company’s work vehicles, wooden ladders may not be the ideal choice.
C) Fiberglass
The Aces of Fiberglass Stepping Stools include
- Solid: Fiberglass is solid and won’t break or fragment. This might be great assuming you really want a dependable stepping stool.
- Non-conductive: A benefit of fiberglass versus aluminum stepping stools is that fiberglass doesn’t direct power. In the event that you work with or close to electrical parts, fiberglass stepping stools might be a decent choice.
- Impervious to encompassing temperature: Fiberglass material doesn’t hold as much surrounding hotness or cold as aluminum. This might be great assuming you intend to involve your stepping stool outside in outrageous hotness or cold.
The Cons of Fiberglass Ladders include
- More pricey: Fiberglass is more expensive than aluminum and wood.
- Fiberglass is heavier than aluminum which causes difficulty in relocating the ladder.
What are Ladder Ratings & Its Importance?
Otherwise called obligation evaluations, stepping stool grades dole out most extreme weight capacities with respect to each stepping stool. These weight counts include the entirety of the accompanying:
- The weight of the worker
- The weight of the worker’s gear or protective equipment
- The weight of tools or supplies carried or kept on the ladder
In total there are nearly five ladder grade categories which are found appreciable and are also recognised by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI):
Type III (Light Duty): This grade holds as much as 200 pounds. Type III is a typical stepping stool for home use on projects with painting, arriving at tall things, moving to a rooftop and that’s only the tip of the iceberg.
Type II (Medium Duty): This grade holds as much as 225 pounds. This type incorporates stepping stools utilized in development and other business provisional labor.
Type I (Heavy Duty): This grade holds as much as 250 pounds. This types is referred to as one of the most frequently utilized type for modern applications that require weighty hardware or stuff.
Type IA (Extra Heavy Duty): This grade can support up to 300 pounds of weight. This type is specifically designed for industrial applications which can require heavier machineries or equipment.
Type IAA (Extra Heavy Duty): This grade can support up to 375 pounds of weight. It helps with jobs that require a lot of heavy equipment or gear.
Observing duty ratings is an important part of staying safe on the job. Choosing the right ladder grade will keep you safe and compliant whether you’re doing a DIY project at home or working on industrial machinery. When perusing a broad assortment of items, duty ratings can also help you narrow down your ladder options.
Ladder Use & Safety Tips
These tips cover best practices from stepping stool choice, examination, set-up and utilize.
A) Tips for stepping stool determination include
1. Pick the Legitimate Length
On most stepping stools, you can’t utilize the highest bar. In the event that utilizing a stepladder or support stepping stool, ensure the second-most elevated advance will give you admittance to what you really want.
2. Close any Gaps
Assuming that utilizing a straight stepping stool or augmentation stepping stool to ascend to where you will venture off the stepping stool and onto a rooftop or design. The stepping stool must reach out the minimum foot higher as compared to the upper point. In the event that there is a hole between the highest point of the stepping stool and the progression point, you risk falling and causing genuine wounds.
3. Overlaps
While utilising any external ladder, you must ensure that the top of the ladder does not extend beyond the highest support. The maximum rise should be three feet. Excessive overlap can function as a lever, causing the ladder’s base to swing out.
B) Tips for stepping stool assessment include
4. Check Before Use
Whether you last utilized your stepping stool a day prior or a year prior, you ought to assess it before each utilization.
5. Elastic Bottom
The elastic covers on the stepping platform which is vital to legitimate the slip-avoidance.
6. Clean Stepping Stool Steps
Excess oil or oil on stepping stool rungs might turn into a slip danger. Clean any apparent particles from the stepping stool steps to save footing.
7. Really Look at Equipment
Inspect a stepping stool’s screws, bolts, rail associations and spreaders to not guarantee anything is absent or broken.
C) Tips for ladder set-up include
8. Level Surface
There is a need to keep your ladder from tilting or toppling, make sure all of its feet are flat on the ground.
9. Reach the Proximity
Proximity is another considerable factor, there is a need to place your ladder close to the work area. There is a possibility of losing your balance which can be higher if you lean or strain to reach the work area.
10. Select Accurate Ratio
It is important to use a safe ladder angle while utilising an extension or any single ladders that can require an upper support point. It is important to keep an aim of a 1:4 ratio and to keep it at a 75-degree tilt. Make sure that the ladder is kept at a minimum distance of 5 feet away from the support point if your ladder is 20 feet long.
D) Tips for ladder use include
11. Actually Look at Yourself
Avoid ascending a stepping stool assuming you feel dazed, weak or debilitated. In the event that something occurs while you are on the stepping stool, you could fall and bring about genuine wounds.
12. Ascend Cautiously
To try not to fall, scale stepping stools gradually and wear clean, slip-safe shoes. While sliding, position your body toward the means and hold the stepping stool sides with two hands.
13. Remain Focused
It might be enticing to attempt to arrive at distant spots while painting or dealing with a stepping stool. In any case, the most secure stance on a stepping stool is to stay in the focal point of the means.
14. Move Cautiously
Be certain to move down prior to repositioning and stepping stool, and do as such with care. Tall augmentation stepping stools might become cumbersome whenever moved rapidly, so take as much time as is needed and enroll help.
15. Use Embellishments
Use stepping stool adornments like utility containers or utility belts to assist with putting away things while chipping away at stepping stools. Endeavouring to rise or drop a stepping stool while holding supplies could make you lose equilibrium and fall.