Wire Stripper (Tool) – Introduction, Types, Parts, Uses & Precautions [Complete Details]
![Wire Stripper (Tool) - Introduction, Types, Parts, Uses & Precautions [Complete Details]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Wire-Stripper-1024x539.jpg)
What is Wire Stripper?
Wire Stripper (Tool) – Introduction, Types, Parts, Uses & Precautions: – A wire stripper is a portable handheld instrument used by professionals, often electricians, to remove the protective coating from an electric wire to replace or repair it. It can also connect the ends of electric cables to other wires or terminals. Professional electricians and allied employees frequently consider a wire remover a crucial instrument. Wire strippers are usually made of steel in various shapes and sizes. Serrated teeth are common, which come in useful for stripping wires. Straight or curved handles are available; most are covered with a rubber covering for a firm grip. Wire strippers frequently include a wire cutter.
Types of Wire Stripper
- Manual Wire Strippers
- Automatic Wire Strippers
- Laser Wire Strippers
1. Manual Wire Stripper

The most versatile is a manual wire stripper, which requires the operator to physically rotate it while exerting pressure around the insulation to cut or modify the wires.
2. Automatic Wire Stripper

One side is maintained straight while the other is cut and removed in an automatic wire remover. A novice can cut and strip most wires fast using an automatic wire stripper.
3. Laser Wire Stripper

Laser wire stripping tools are a high-end alternative to traditional insulation removal options when highly accurate work is required. This could include cabling with a very small diameter, extremely robust insulation material, or unique cabling, such as cabling for medical equipment. The tool’s laser radiation vaporizes the insulation material, but the interior components are extremely reflecting and thus unaffected by the standard beam. A separate laser can be used to cut the cable if it has any metal shielding. Desktop laser wire strippers are the most common. Models differ in terms of capabilities and specializations.
Some wire strippers can be set to repeatedly strip the same size of wire, which can save time. Self-adjusting strippers can strip practically any size wire without selecting a specific slot or making other changes.
Coaxial wires require a special type of stripper. Extra-large commercial-grade wire can be stripped with power strippers. Wire strippers differ primarily in terms of the wire size they can handle and the additional tool functions. Electricians normally have a variety of wire stripping, cutting, and crimping equipment, but wire strippers like the one pictured above are the most prevalent among them.
Some Different Types of Manual Wire Strippers
1) Adjustable Strippers
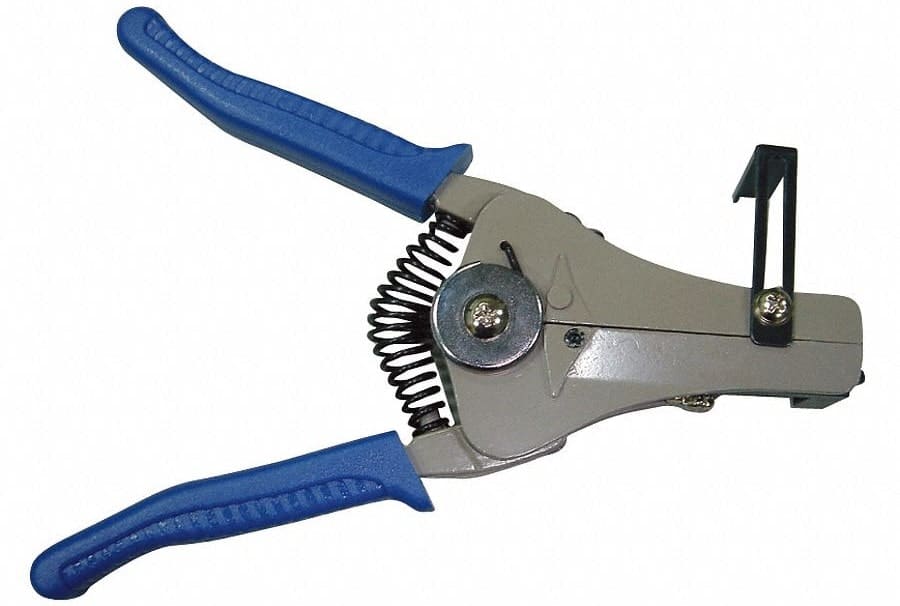

Insert a wire, and the device will automatically adjust to accommodate; however, precise manual adjustments can also be made.
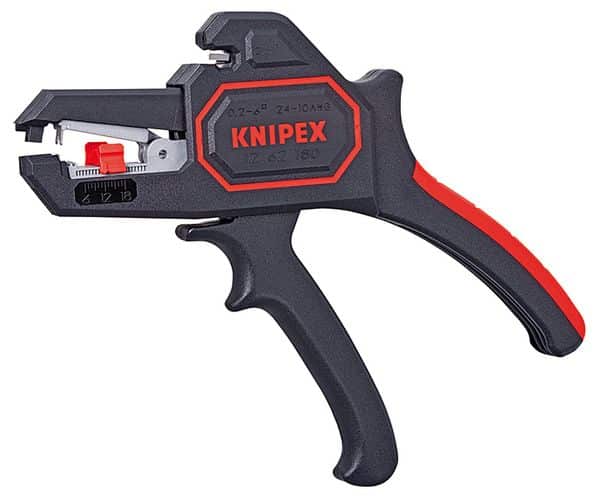
2) Triple Action Strippers

These professional models offer spiral, linear, and rotary cutting actions. Spiral is especially good in stripping materials like rubber.
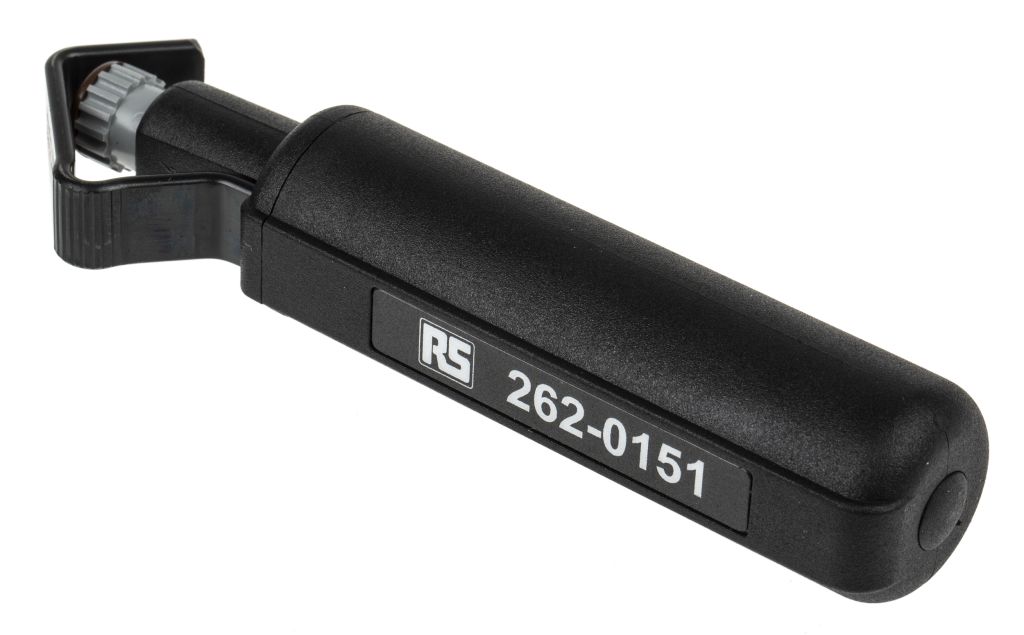
3) Pistol Wire Stripper

Self-adjusting blades grasp and remove cabling in a single action on certain versions.
4) Sheath Strippers
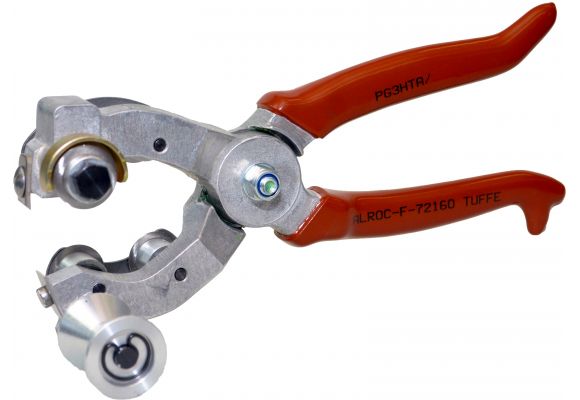

Sheath strippers, unlike triple-action models, provide a simple yet effective rotary cut, making them perfect for two and three-core leads and cables. They usually auto-adjust for different diameters as well.
5) Insulated Strippers

These have VDE handles, an industry-standard certification indicating that they are electrostatic discharge-resistant.
6) Steel Armored Strippers
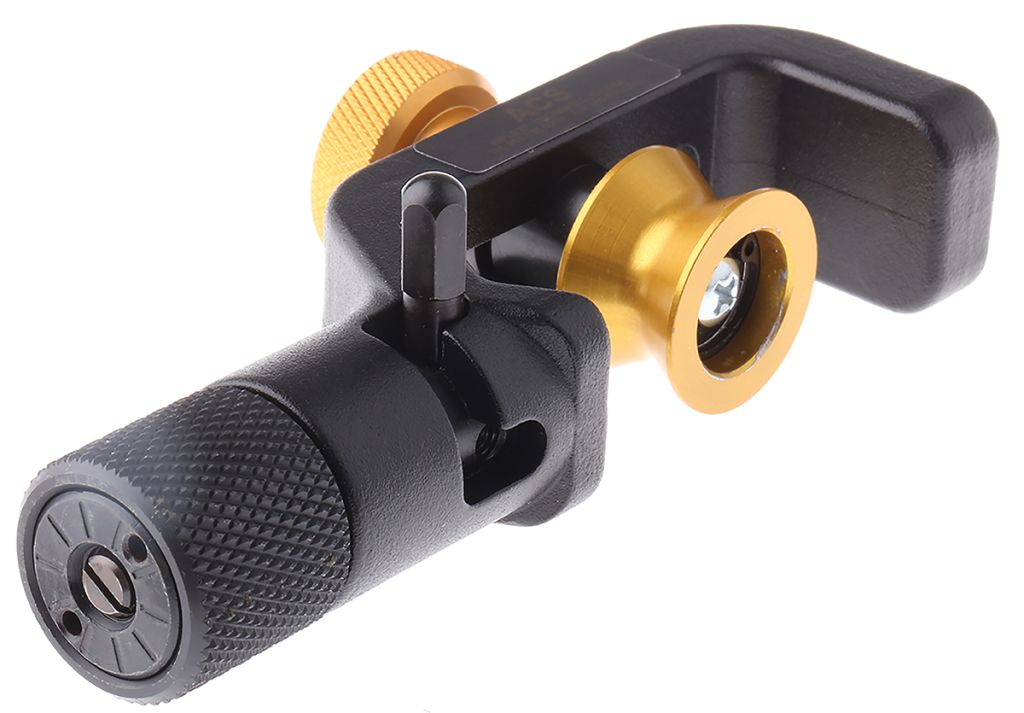

These tools have a strengthened blade designed to cut through steel, copper, or aluminum shielding and conduits in fiber optic and armored cable shielding.
Parts of Wire Stripper
- Tip or nose for holding, twisting, or creating hooks or loops in wire
- Various size stripping blade slots
- Wire cutter
- Small bolt shear (usually 6/32 and 8/32)
- Crimpers for crimp connectors
- Loophole to create hook or loop in a wire for screw terminals
- Ergonomically shaped handle
How to Use Wire Strippers
Wire stripping is a necessary and routine task for electricians and engineers, but safety is paramount, as with any electrical equipment task. Wire strippers are made to be safe. Smaller wires can be stripped using a sharp knife, but wire strippers, as a specialized tool, are significantly safer and reduce the chance of injury.
a) Determine the Gauge and Type of Wire
To begin, determine the gauge of the wire is stripped. This information is printed on the insulation. The gauge will be given a numerical value. It’s also important to know if the wire is solid or stranded.
b) Make Sure the Wire is the Right Length for the Tool
The wire gauge must then match the matching hole on the wire remover. This step is crucial because if the hole is larger than the wire gauge, the insulation will not be completely cut, and stripping will be difficult. If you choose a hole smaller than the wire gauge, you risk nicking the wire and compromising it.
c) Set the Wire in Place
The stripper will cut through the wire insulation as you slowly press the handles together.
d) Remove the Insulating Material
Remove the insulation from the wire with a slug remover.
Stripped Wire Precautions
The machinery used to create a stripped wire greatly impacts its quality. The simplest technique to create a high-quality exposed conductor is to use appropriately sized equipment, and many wires must be gauged. The strip length is another factor that determines wire quality. Strip gauges will be built into switches and receptacles, and automated equipment will have a transparent adjustment mechanism to assure precise wire and strip lengths.
Wire strips that are too short will have an insecure connection, which could result in overheating, arcing, and a circuit failure; conversely, conductors that are overexposed provide an electrocution risk. Conductors that are damaged during the stripping process pose a major risk. Temperature variations in the conductor cause cracks, nicks, and scratches. Overheating will occur if the same current level is carried through a smaller wire cross-section. Finally, wire damage, such as frayed or squeezed insulation, will reduce wire performance.
Conclusion
The work determines the best electrical wire stripping tools at hand. You can’t afford to spare on safety or dependability regarding electrical tools. Wire strippers ranging in diameter from 0.02mm to 70mm are available for purchase and are perfect for electrical cable installations, telecommunications equipment, and other applications. Stripping or cutting live wires is not a good idea because it can be quite harmful. On the other hand, professional electricians are occasionally forced to work with live wiring, and several kinds of strippers and pliers have electrically shielded handles for this purpose.