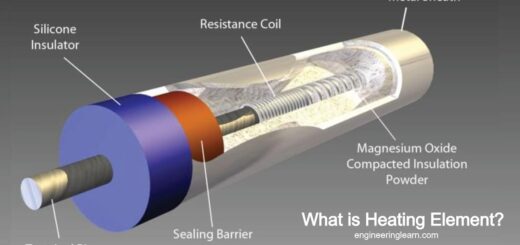
How does Induction Heating Work? [Explained]
![How does Induction Heating Work? [Explained]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/How-does-Induction-Heating-Work-1024x539.jpg)
Introduction
How does Induction Heating Work? [Explained]: – Induction heating systems with fundamentally higher viability are expected with the improvement for development of semiconductor. In addition, special coil shapes and designs provide expanded productivity. The point of these efforts is to work on the performance as well as the reliability of the induction heating systems. They are precisely designed induction coils collaborated with a strong and flexible induction power supply to produce repeatable heating outcomes intended for the ideal application.
Induction power supplies designed to precisely measure material heating and respond to a material’s property changes during the heating cycle make accomplishing different heating profiles from a solitary heating application a reality. With the assistance of induction heating, heating the metals to their melting point in a suitable furnace is conceivable. In the present time, induction has had its spot in the industrial economy for the purpose of speeding part production, diminishing creation costs, and accomplishing quality outcomes.
What is Induction Heating?
The currents when induced in the material by electromagnetic action is further utilized to heat it is known as induction heating. It is a contact less electric heating strategy wherein the material will be heated without connecting with the supply. The operation or activity of induction heating relies upon the standard of AC transformers. of induction heating plays a very prominent role in solidifying a part to prevent any kind of wear, which further makes the metal malleable for forging into the best shape; two parts together are brazed, melt and blend the ingredients which go into the high-temperature alloys, making jet engines conceivable; or for quite a few different applications.
Set forth simply, induction heating is a method for heating an object utilizing electricity. This process has numerous applications, including cooking, welding, and heat treating. Induction heating can be utilized for the majority of different purposes and across a wide range of industries including:
Automotive
Induction heating is utilized for hardening or solidifying and tempering gears, shafts, and other car parts.
Food and Beverage
Induction heating is utilized in food processing for cooking, sanitizing, and sterilizing.
Manufacturing
Induction heating is utilized in welding and heat- treating metals.
For specialty metal applications, induction heating is perfect which includes components like titanium, valuable metals, and high-level composites. The exact heating control accessible with induction is unparalleled. Further, involving similar heating fundamentals as vacuum crucible heating applications, induction heating can be conveyed under the atmosphere for persistent applications. For instance bright annealing of stainless steel tube and pipe. An induction system improves working conditions for your employees by wiping out smoke, waste heat, poisonous emanations, and loud noise.
How does Induction Heating Work?
How precisely does induction heating work? It assists with having a fundamental understanding of the standards of electricity. An alternating magnetic field is applied when an alternating electrical current is applied to the primary of a transformer.
If we talk about what’s inside the coil, the material which needs to be hated is positioned in it. The induction work coil is water-cooled and doesn’t touch the heated material. The power supply is utilized to convert direct power completely to alternating current.
A high frequency or recurrence alternating current to the electromagnet is sent by an electronic oscillator. The coil receives an alternating magnetic field. This magnetic field transfers the material, or conductor set up for heating. An electric current, otherwise called an eddy current, is produced in the conductor. By the flow and circulation of eddy currents through the material resistance, the conductor is heated further. This is otherwise called Joule heating. Ferromagnetic metals like iron can likewise heat up by magnetic hysteresis losses.
The initial or underlying high electric current recurrence might vary relying upon many factors, for example, the kind of material to be heated, level of depth or profundity for heating, the connection type between conductor and coil, and furthermore the size of an object.
Metals, semiconductors, and furthermore non-conductors are some of the materials used for heating. Glass and plastic are non-conductors.At first, induction is utilized to heat another conductor if you want to heat material with low or no conductivity, A material that can transfer heat to the non-conductive material is a well-known material I.e. graphite.
As the induction heating process is a non-contact heating process the material to be heated can be accessible, away from the power supply or lowered in a fluid or in any gaseous environment or in a vacuum. This kind of heating process requires no combustion gases.
Induction heating is useful as well as helpful for some kinds of processes. It tends to be utilized where an exceptionally low temperature is suitable, and furthermore for different processes where temperatures may need to be pretty much as high as 3000 degrees Celsius. Contingent upon the process and specifications, heating processes might require numerous months, or just a small portion of one moment to finish.
Conclusion
Technological advancement or progressions made the induction heating process a valuable tool in the industry of heat treatment plants. This strategy is more exact or precise for the surface hardening of metals and nonferrous metals. An extensively notable usage of induction heating is induction cooking which offers cooking with a negligible scattering of heat in the environmental factors. Close by this, induction heating is used to manufacture, welding, binding of metals, as well as brazing different metals. It is similarly used in the hardening of steel, sintering, sterilization of clinical equipment, and so forth.
For manufacturing industries, induction heating provides a strong pack of consistency, speed, and control. This is a flawless, rapid, and non-polluting heating process. The efficiency and productivity of induction heating for an explicit application rely upon how much temperature change is required. An extensive range of temperature changes can be accommodated; as a guideline, more induction heating power is for the most part used to increase the degree of temperature change.
Image Source: – engineeringclicks, ultraflexpower