Connecting Rod: Types, Function, Material & Problems
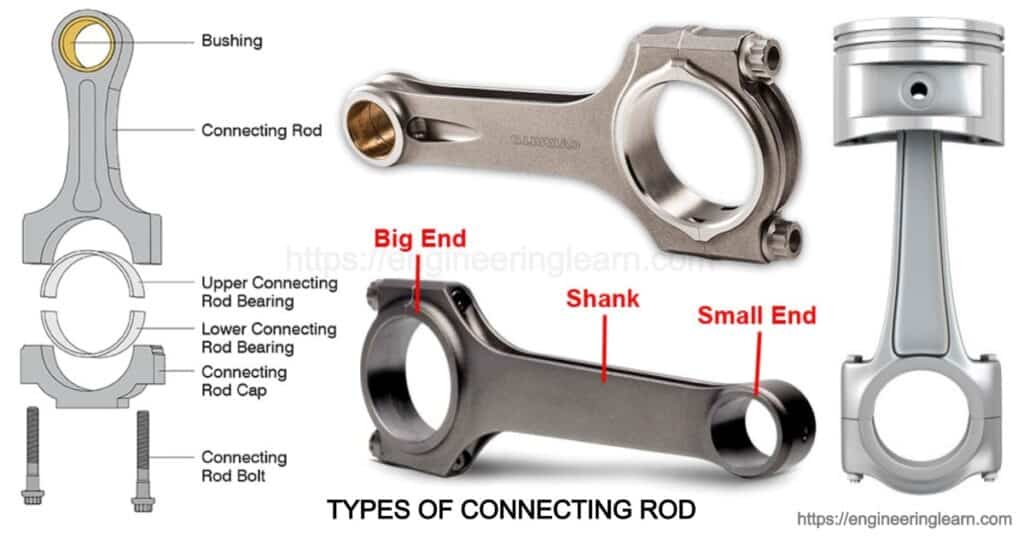
What is Connecting Rod?
Connecting Rod: Types, Function, Material & Problems :- crankshaft and which should exhibit the properties of high strength, low inertial mass and uniformity of mass with all the other connecting rods that are attached to the crankshaft. Coupling of the crankshaft is done using the half shells solid journal bearing which is inserted on both the sides of the split large end. The coupling to the piston is mostly through a quite hard steel gudgeon pin via piston body.
The large ends of a connecting rod are mostly threaded directly in such a way that the split portion can be attached during the assembly with the crankshaft. The material of a connecting rods includes a powder metallurgy steel which are designed into an initial shape which then forged to the final dimension wherein the medium is the carbon steels and are found developing superior strength either through a separate heat treating processes or by controlling the forging step.
Considering the racing engines it may utilize titanium alloys for connecting rods so that it can achieve a high ratio of strength to mass of the part.
Function of Connecting Rod
The first steam engine or an atmospheric engine was first found in the year 1712 which used chain drive rather than a connecting rod as its piston was only responsible for producing the force in a single direction. Whereas most of the steam engines amongst these are double-acting and the force is kept producing in both the directions which leads to the use of a connecting rod. The specific arrangement is done for a large sliding bearing block which is also referred to as a crosshead with the hinge within the piston and the connecting rod that is placed outside the cylinder and requires a seal around the piston rod. (Function of Connecting Rod)
A connecting rod for an internal combustion engine includes a big end and small end rod. The small end is found attached to the gudgeon pin which is also referred to as piston pin or wrist pin that may pivot in the piston. Whereas on the other end the big end connects to the crankpin with the help of a plain bearing which reduces the amount of friction, however the smaller engines are found using a rolling-element bearing which helps in avoiding the need for a pumped lubrication system. There is a pinhole which is bored through the bearing on the big end of the connecting rod so that the lubricating oil can squirt out onto the thrust side of the cylinder wall in order to lubricate the travel of the pistons and the piston rings. (Function of Connecting Rod)
A connecting rod is also found rotating at both the ends, so that the angle between the connecting rod and the piston can be changed, as the rod moves up and down and rotates around the crankshaft. (Function of Connecting Rod)
Material Used in Connecting Rod
The materials which are used in making of a connecting rod varies widely which can include materials like carbon steel, iron base sintered metal, micro-alloyed steel and graphite cast iron. The connecting rods in mass-produced automotive engines are most commonly built up of steel. In most of the high performance applications, billet connecting rods are used, that are machined out of a solid billet of metal, instead of being casted or forged.
Other materials are those which include aluminium alloy that can be used for lightness and to also absorb its high impact at the expense of durability. Other than this, Titanium is also an option which is quite expensive option and is found reducing the weight whereas on the other side the cast iron is found to be cheaper and has very low performance applications like scooters.
Radial engines are found using master-slave connecting rods, wherein the uppermost piston in the animation is accompanied with a master rod and a direct attachment to the crankshaft. All the other remaining pistons pin attach their connecting rods to the rings which are present around the edge of the master rod.
Multi-Bank Engines
Multi bank engines inculcate many cylinders, like a V12 engine, which have a very little space that is available for many connecting rod journals of a limited length of crankshaft. The simplest solution which has been implied to most of the road car engines is for each pair of cylinders in order to share a crank journal that creates a rocking couple. The master-slave connecting rods includes one or more ring pins which are connected to the big ends of slave rods on other cylinders.
A drawback of master-slave rods is that the strokes of the slave pistons will be slightly longer as compared to the master piston, which is found increasing the number of vibrations in the V engines. The most complicated example of master-slave connecting rods is referred to as the 24-cylinder Junkers Jumo 222 experimental airplane engine which was developed at the time of World War II. This engine includes six banks of cylinders with each having four cylinders per bank. The each layer of six cylinders is found using one master connecting rod, including the other five cylinders by using the slave rods. There are almost 300 test engines that were built whereas the engine did not reach production.
Fork-Blade Rods (Split big-end Rods)
Fork blade rods are also commonly known as split big-end rods, which have been used on V-twin motorcycle engines and V12 aircraft engines. Mostly for each pair of cylinder, a fork rod is split in two at the bigger end and the blade rod from the opposing cylinder is made thin in order to fit in the gap of the fork. This arrangement helps in removing the rocking couple which is caused when the pairs of cylinder are offset along the crankshaft.
One of the most popular arrangement for the big-end bearing is for fork rod in order to have a single wide bearing sleeve which spans the entire width of the rod and also includes the central gap. The blade rod then moves indirectly on the crankpin via outside of this sleeve. This results in two rods to oscillate back and forth that are responsible for reducing the forces on the bearing and the surface of the speed. Moreover the bearing movement also becomes reciprocating instead of continuous rotation that is found to be more difficult problem in the case of lubrication.
Types of Connecting Rod
The connecting rods are also named as Conrod which are found to be of various types, based on the type of material they are made of. So, here are some various types of connecting rod which are available and about which one should definitely know:
1. Billet Conrods: ( Types of Connecting Rod )
The billet connecting rods refers to a machine which is obtained from one piece of steel or aluminum. It is comparatively lighter, stronger and durable as compared to other kinds of con rods. These connecting rods are commonly used for high-end running vehicles wherein the product is designed in order to reduce the stress risers and to ease it into the natural grain of billet material.
2. Cast Rod: ( Types of Connecting Rod )
Cast rods are referred to as the those connecting rods which are more preferred by manufacturers as it is capable of handling the load of the stock engine. The estimated production cost of these connecting rod is quite less but on the same time it cannot be used in high horsepower applications ranging from 450 to 6,000 rpm. A cast connecting rods is found containing a noticeable seam down in the middle which is used for differentiating it from the other forged type.
3. Forged Rod: ( Types of Connecting Rod )
Forged rods are referred to as those connecting rods which are made of forging or by forcing grain of selected material into the shape of the rod. The material which is mostly used is either a steel alloy or aluminium which depends upon the required properties.
The manufacturers of the forged rods use various types of steel alloys, chrome and nickel alloys wherein the end product is not found to be brittle. Nickels or chrome alloy are responsible for increasing the strength of a connecting rod.
Problems of Connecting Rod
The connecting rods are found experiencing a problems while working as it experiences different levels of stresses during the combustion chamber. Most of these issues are fixed whereas some on the other hand require a complete change of the connecting rod. The rod is stretched and compressed, which is found causing the con rod to break which can completely damage the engine. So, below mentioned are the failures which can occurs in a connecting rod:
1. Fatigue
This is one of the foremost reason why a connecting rod breaks. This occurs mostly in the old engines. The process of compression and stretching of the rod takes place thousands of time in a minute which eventually causes wear and tear to the part until it ends up breaking. Lack of oil and presence of dirt in the engine can be one of the major cause of fatigue.
2. Hydro lock
The condition of hydro lock occurs when the water penetrates into the piston chamber and leads to deformation of the connecting rod. This condition occurs when the vehicle drives through a flooded street. Even a little quantity of water in the cylinder can cause knocking or tapping sound which can be repaired easily. Whereas, if there is a lot of water found in the cylinder, all the space for spark time will be taken which might cause the cylinder rod to bend or snap.
3. Over Revving
Over revving is referred to as that type of failure which occurs in mostly new and high-performing engines. In case the tachometer shows red, it will indicate the condition of the connecting rod which seems to be in danger. This can happen due to the forces which act on the con rod and increase dramatically at a high revolution.
4. Pin Failure
The piston pin is referred to as the one which is connected to the connecting rod inside the piston which can cause failure. In some engine this can result in catastrophic engine failure when the connecting rod moves into the engine block or when the crankshaft is bent.
Image Source :- Bikesmedia, Pngio, Costex