5 Types of Brick Masonry – Definition, Brick Bond, Advantages & Disadvantages [Complete Guide]
Definition of Brick Masonry?
Types of Brick Masonry: Definition, Brick Bond, Advantages & Disadvantages :- Brick masonry can be defined as the systematic arrangement of bricks with the help of mortar. It can be used with clay as well as mortar. It is cheaper in place where clay is available in abundance. Brick masonry provides better fire resistance, light weighted in comparison to stone masonry. Bricks are of uniform in size so not much skill is required for its construction.
The conventional size of brick is 23cm x 11.4cm x 7.6cm. Lengthwise face (Long narrow face) of brick is known as stretcher and width wise face of brick is known as header. Frog in brick helps in providing proper adhesion between layers by acting as a key. It also helps in printing the name of the trader.
Different Types of Brick Masonry
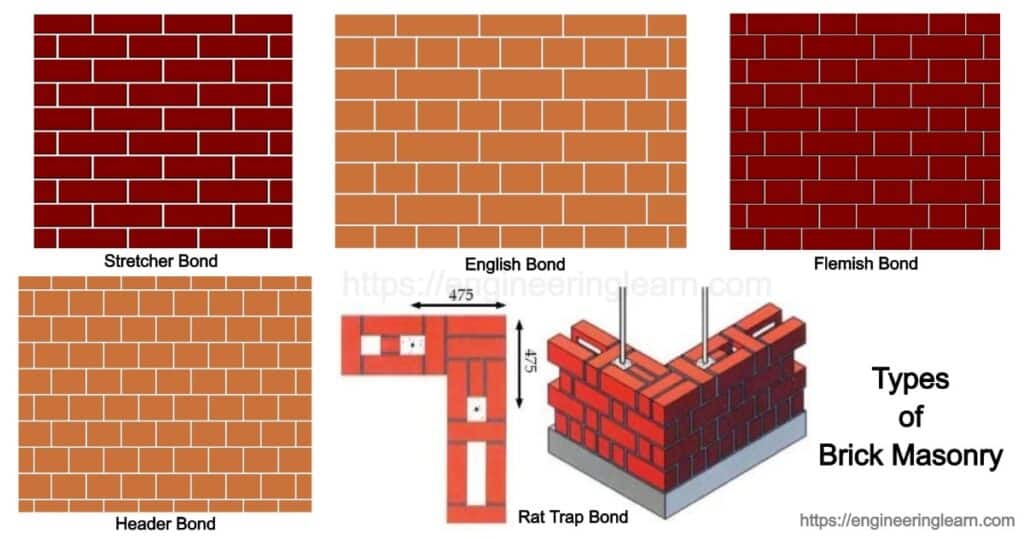
1. Stretcher Bond ( Running Bond )
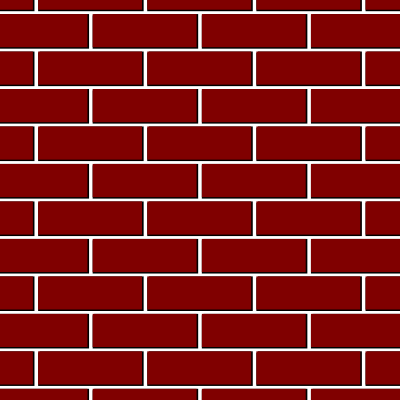
- Stretcher bonds wall have very less strength so that they cannot stand alone when they have long span and height. Therefore they need structure like brick masonry columns at regular intervals to support them.
- Stretcher bonds are generally used for outer facing in framed structure of steel or reinforced concrete. They are commonly used for gardens, boundary walls because their strength is relatively low therefore they are not used for bearing walls.
- It is constructed when bricks are arranged with their stretchers showing, and overlapping is done at midway with below course and above course.
- It is suitably used for half brick thick wall.
- Overlap is of half brick and half bat is used for breaking the alignment.
- Bat is a portion of a brick cut across the width, and half bat is bat with length half of the brick’s original length.
- It takes lesser space and economical.
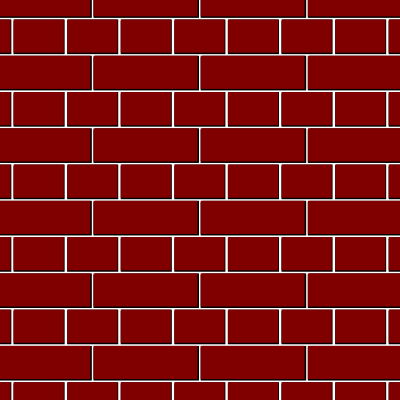
2. Header Bond
- Header is the shortest square face of the brick.
- In header bonds, the bricks are arranged as headers on wall face in each course.
- They are used for construction of walls with full brick thickness.
- Overlap will be of one forth and three forth bat will be used for breaking the alignment.
- Their strength is more than stretcher bond
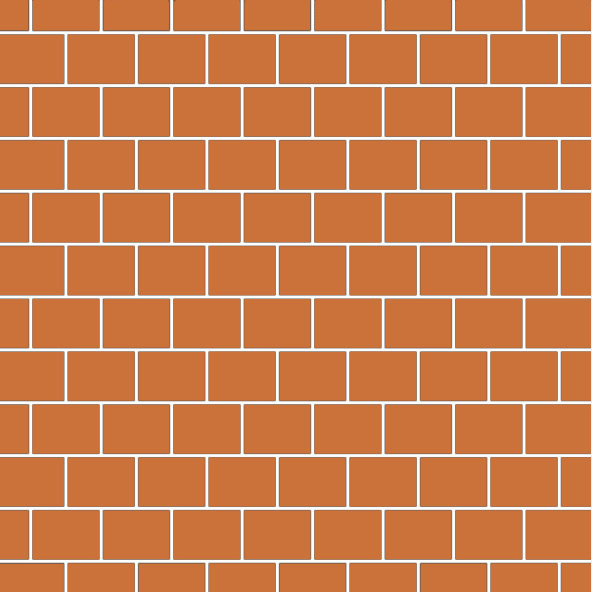
3. English Bond
- The bricks are placed in such a manner that every alternate course consist of header and stretcher.
- Quoin closer is provided at the starting and end of the wall in vertical joints to break the continuity.
- A quoin closer in a brick is a type of brick which is cut into two halves lengthwise and it is used in corner portion of walls.
- Thickness will be minimum one brick.
- Overlap will be one forth brick.
- For the wall thickness more than or equal to one and half brick English bond is strongest.
4. Flemish Bond
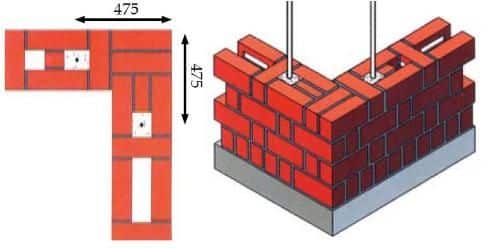
- It is also called as Dutch bond.
- In this type of bonding every course consist of header and stretcher.
- Queen closer is used to break the alignment.
- Minimum thickness of brick wall will be one brick but generally one and half brick thick brick wall is preferred in case of Flemish bond to utilize the half bat inside the brick wall.
- The main disadvantage of Flemish bond is that their construction is difficult and it requires greater skill to arrange it properly.
- They have better aesthetic but for load bearing wall construction they are weaker than English bond
5. Rat Trap Bond
- Rat trap bond is a brick masonry method of wall construction just like English bond and Flemish bond but having a different set of rules and regulations for laying the bricks.
- In rat trap bond the bricks are placed in vertical position, while as we saw in English bond and Flemish bond or other bonds the bricks are laid horizontally, which means if the size of the brick is 230mm x 115mm x 75mm then the 75mm x 230mm surface of the brick will be acting as a base for the brick in the rat trap bond.
- Due to the vertical positioning of brick, cavity is created within the wall of one brick thickness.
- It is named as rat trap because rats are trapped very easily in space provide between network provided in the wall.
- The arrangement of the bricks in rat trap bond is similar to double Flemish bond in one brick thickness.
Types of Brick Masonry
- The first two stretchers in double Flemish bond in laid on 115mm x 230mm surface. And on the rat trap bond, same bricks are laid on the 75mm x 230mm surface and because of this the height of wall increases automatically in every course and ultimately decreasing the number of bricks used in the same surface of wall with any other bond.
- Also due to the hollow surface in between, the area used for cement is also reduced and due to the cavity inside, it gives good thermal comfort inside the building.
- It should only be done by the masons who are trained in rat trap bond otherwise there will be wastage of mortar falling into the gap while working.
- We cannot use concealed wiring or plumbing, due to the complex brick network inside.
- If we break any one brick many other bricks will fall down or crack which will reduce the strength of the wall.
- Two rat traps will be joining at 90 degree by placing two stretchers together at the junctions and after that we follow the same rat trap bond pattern. This will create our course- 1 and in course- 2 we start with placing two headers at the corner, and after that we can continue the same rat trap bond pattern and at last we put the courses one above another of the wall to get the overall appearance of the wall.
Advantages of Brick Masonry
- It requires approximately 30 percent less bricks and 50 percent less mortar than conventional masonry, which reduces the cost of wall by 20- 30 percent.
- Their strength is equal to a standard solid brick wall.
- The cavities provided inside the walls act as thermal insulators. Thus the interiors are cool in summer and warm in winter.
- It can be used for thick partition wall as well as walls for load bearing.
Disadvantages of Brick Masonry
- Due to formation of cavities in the masonry building it does not provide good sound insulation.
- Wall length designing should be done with extra care.
- On average rat trap brick wall needs cleanness of external surface in every three years.













