Lights of Car | Headlights of Car | Types of Headlights | Types of Headlight Bulbs [with Names & Pictures]
![Lights of Car | Headlights of Car | Types of Headlights | Types of Headlight Bulbs [with Names & Pictures]](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Lights-of-Car-1024x539.jpg)
What are Headlights on a Vehicle?
Lights of Car | Headlights of Car | Types of Headlights | Types of Headlight Bulbs [with Names & Pictures]: – In the dark, a car’s headlights are its primary illumination source, which is critical for drivers to see the road ahead. The two main components of most headlights are the projector, which houses the light bulb, and the reflector, which helps direct the light back into the projector.
Halogen headlights are standard equipment on the majority of today’s automobiles. The filament in this headlamp is heated by electricity until it emits light. The gas within the headlight’s glass envelope also affects the filament’s ability to glow.
The most popular headlights are halogen. However, there are numerous options. Using LED headlights is one example of this. A current is fed through them to make the diodes light up. Compared to incandescent lights, LEDs are more energy-efficient and may last up to many years before needing to be replaced.
Significance of Automobile Headlights: ( Lights of Car )
One of the most critical functions of a car’s headlights is seeing the road ahead at night or in poor visibility situations like fog or rain. Whether using headlights, drivers can better see possible dangers and make sound judgments about when to slow down or accelerate. Additionally, safe driving at night or in poor weather conditions needs working brakes and tyres, but if you can’t see where you’re going, none of that matters.
2 Different Designs for Driving Lights: ( Lights of Car )
There are two primary styles of headlamp design. There are two types of headlights: reflector and projector.
- Using a parabolic reflector, a light source is installed in a plastic or glass lens with a succession of tiny, carefully ground mini-lenses. This directs the amplified light from the reflector to illuminate the road ahead of the vehicle adequately.
- • When using projector headlights, the light is emitted from a lens in front of the source.
In 1984, composite (plastic) headlight assemblies took the place of the previous round or square glass headlamps. Federal law changed to fit the contours of the vehicle’s grille and fenders so that carmakers could form the headlights in various ways.
Types of Headlight Bulbs: ( Lights of Car )
LED, Xenon/HID and Laser are the most prevalent car headlight bulbs. What sort of headlight bulb do I need for my car? Here’s a simple guide to help you choose what type of headlight bulb to get:
Halogen, LED, Xenon/HID, and laser are the most prevalent automotive headlights.
1. Halogen: ( Types of Headlight Bulbs )
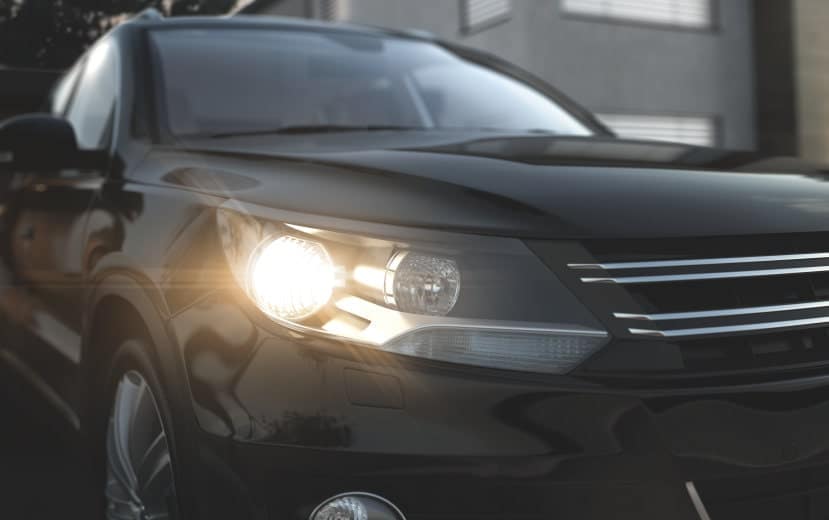

This light bulb uses pressured gas rather than a vacuum to create a filament or a pair of filaments that may be used for both brilliant and dim headlamp functions. While incandescent lights’ filaments are made of inert tungsten, halogen bulbs, with their iodine- or bromine-reactive halogen gas filling the bulb’s glass envelope, burn brighter and longer without discolouring the interior. Certain halogen lights contain a blue coating to look more optimistic than they are.
Halogen bulbs are used in the majority of contemporary headlights. Instead of the original filament type, some sealed beam replacements for older cars with glass use halogen capsules incorporated into the closed beam case. Those old-style filaments will oxidise and burn out very instantly if one of those early sealed beam units is punctured by a rock. It doesn’t matter if the lens has a little rock hole in it since the halogen capsule is delivering the light.
Halogen bulbs are used in the majority of contemporary headlights.
Pros of Halogen:
However, halogen lights don’t cost much to make and are generally less than $20 per bulb for replacement, but only the best-known brands will last longer. On most automobiles, these can be changed. Removing items from the engine compartment or splash shield may be necessary for certain cars.
Cons of Halogen:
- The colour temperature of standard halogen headlights is around 3,000 Kelvin, giving off a mild yellowish glow. However, most sites do not permit the use of bulbs with a Kelvin temperature of 3,400 to 4,200.
- The whiter the light, the higher the Kelvin temperature. While the Kelvin scale may go up to 10,000, that’s the brightness of intense sunlight under a blue sky, not the intensity of automobile headlights. If you want bright white lights with a broader range, you may want to choose a higher Kelvin headlight bulb. This is a beautiful, comfortable glow that performs the job effectively.
- Manufacturing halogen lights are inexpensive, and each bulb can be replaced for less than $20.
- The typical lifetime of these bulbs is between 450 and 1,000 hours, which is lower than regular headlight bulbs.
- The average bulb costs $10 to $20, while a pair of headlight components may cost as little as $100.
2. LED: ( Types of Headlight Bulbs )
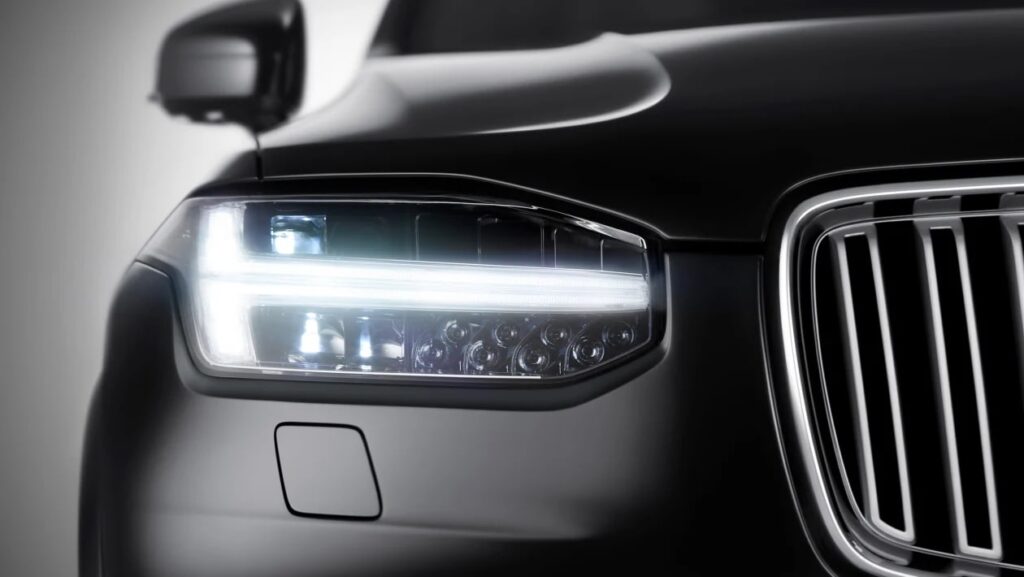

Electroluminescence, a fancy name for what means that electrons are shot toward positively charged holes in a semiconductor, illuminates LED (Light-Emitting Diode) headlight bulbs. This energy is then released in the form of photons, which are light particles.
Dashboard lighting and screen consoles now use the same technology. LED lights have expanded beyond flashlights and indicator lights on appliances, including stop lamps, tail lamps, interior lamps, and even residential ones. This means that LED lights have become ubiquitous.
Electroluminescence is used to illuminate LED (Light-Emitting Diode) headlight bulbs.
Pros of LED:
- Small semiconductors may be combined in various ways to create LED bulbs, which are ideal for confined locations. Using this technology, manufacturers can generate sleeker headlamp designs and more options for decorating other assembly components, such as turn signal lights.
- It is possible to create LEDs that produce any hue in the visible light spectrum. Oncoming traffic is not blinded by the intense, white light they emit, which may illuminate up to a mile ahead. LED lights typically have a colour temperature of between 4,000 and 6,000 Kelvin.
- In addition to this, they are energy-efficient and can be turned on and off in seconds.
Cons of LED:
- Due to the higher cost of LED headlights, they are often more expensive than halogen lights. Because of the heat sink that must be integrated into the sunshine to keep the base-emitter from overheating, the structure of their assembly is somewhat different.
- Small semiconductors may be combined in various ways to create LED bulbs, which are ideal for confined locations.
- Longevity: between 10,000 and 30,000 hours on average (some sources put the life at 5,000 hours). LED bulbs operate more excellent and emit less heat than halogen headlights. In certain situations, this might extend the life of a vehicle’s lights for its entire service life.
- The average price for a bulb is $100, while a pair of headlight assemblies may cost between $600 and $1,300.
3. Xenon / HID: ( Types of Headlight Bulbs )
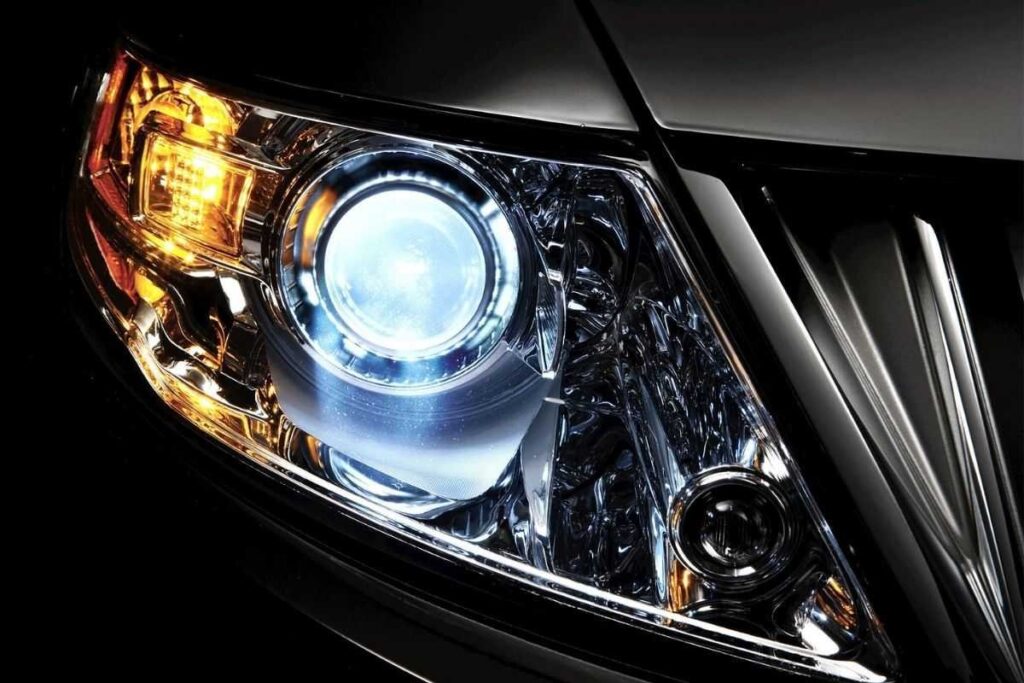

It is not uncommon for high-end automobiles to be equipped with Xenon headlights (also known as HIDs or High-Intensity Discharge lamps). Xenon and argon gases are combined with evaporated metals to produce an incredibly brilliant light in these headlights. Xenon/HID headlamp conversion kits are available from aftermarket vendors.
HID lights, or High-Intensity Discharge lights, are a kind of headlamp typically seen on high-end automobiles.
With HIDs, you may get a broader spectrum of lighting since they produce light in a bluish-white colour (4,000-6,000 Kelvin).
Cons of HID:
- Xenon or HID headlights take several seconds to achieve full brightness. They may also be overly bright, causing other motorists to be blinded.
- The other motorist may have difficulty seeing you because of the bluish-white glare. You may not be able to see anything beyond the headlights’ area of illumination since their light is so concentrated. This may make parking, switching lanes, or crossing junctions more difficult.
- Headlights with xenon and argon gas mixtures and evaporated metals provide a brilliant light.
- There is a typical life lifetime of between 2,000 and 10,000 hours. Because HID headlights have no filament that might burn out, they can survive for a long time.
- A pair of headlamp assemblies may cost anything from $350 to $1,400.
4. Laser: ( Types of Headlight Bulbs )
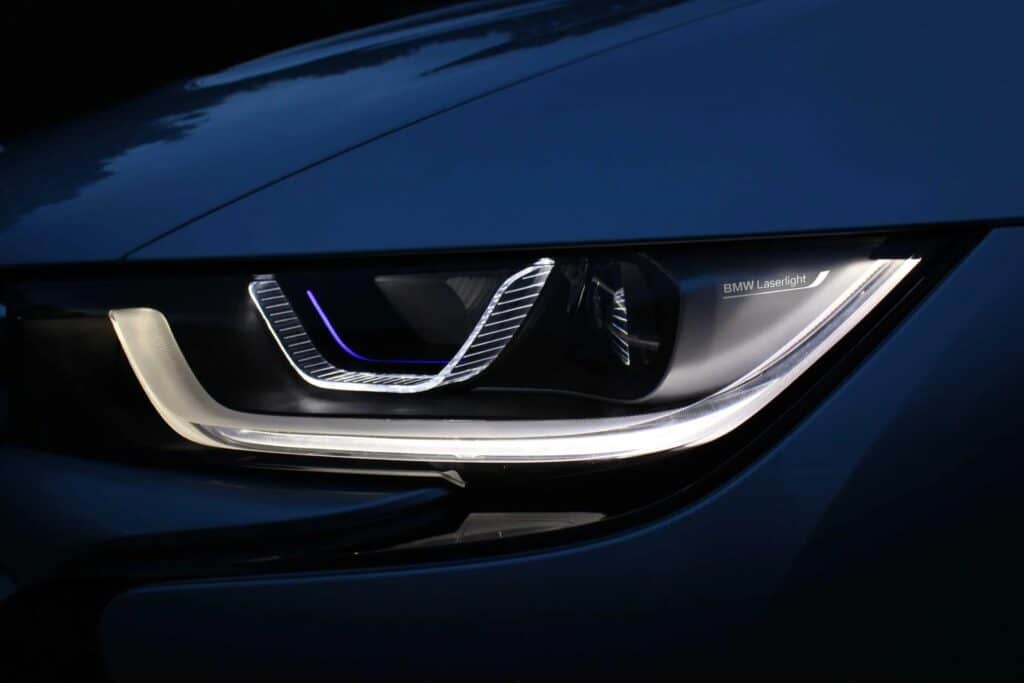

Currently, laser headlights are a relatively new development in automobile illumination. Chemiluminescence is the mechanism used by these lights to create light, and it is a relatively simple one.
The phosphorous gas within a chamber glows due to the laser beams. The light coming from the gas is what you see in front of your car, not the laser beams themselves.
Instead, lasers within the headlight unit illuminate mirrors, reflecting light onto a lens filled with a specific gas to produce a powerful light beam.
Pros of Laser:
The efficiency of laser headlights is superior to that of LED bulbs. They can create 1,000 times as much light as LEDs while using half the energy. As a result, manufacturers may build a shallower assembly since they are 10 times smaller.
They have a wide range, are adaptable, and can be quickly turned on and off.
Cons of Laser:
LEDs create less heat than incandescent bulbs, yet incandescent bulbs produce more heat than LEDs. This necessitates the use of more advanced cooling technologies in assembly.
It is also important to note that they are presently only available for usage in high beams, which necessitates the use of standard halogen, LED or HID headlights.
Even though BMW and Audi have begun employing them in a few models, they were only recently given the green light for usage in the United States. They are much more costly than other headlights and might cost thousands of dollars.
Hours: 50,000 hours on a typical battery. Laser headlights have a long service life because of their low energy consumption.
Cost: $8,000 to $12,000 on average.
Car Headlights Provide Several Advantages
There are several advantages to using the headlights of a vehicle. Whether using headlights, drivers can better see possible dangers and make sound judgments about when to slow down or accelerate. Additionally, safe driving at night or in poor weather conditions needs working brakes and tyres, but if you can’t see where you’re going, none of that matters!
When vision is limited, car headlights may be a helpful tool. To help drivers see the road ahead in these circumstances, headlights may provide the additional illumination they need. Finally, many motorists find their vehicle’s headlights’ aesthetic appeal significant.
Conclusion: ( Lights of Car )
Car headlights are an essential safety component but must be utilised with care. Automobile headlights are an essential but dangerous safety device. Whether using headlights, drivers can better see possible dangers and make sound judgments about when to slow down or accelerate. There are times when driving in foggy or rainy circumstances may be dangerous. Thus additional care should be exercised as necessary. Additionally, safe driving at night or in poor weather conditions needs working brakes and tyres, but if you can’t see where you’re going, none of that matters.
Image Source: – osram, autoexpress, philkotse, paultan