Solenoid Valve: Types, Parts, Operation, Working, Applications, Materials, Advantages & Disadvantages
What is a Solenoid Valve?
Solenoid Valve: Types, Parts, Operation, Working, Applications, Materials, Advantages & Disadvantages :- These valves are electromechanically operated valves. Solenoid valves differ in properties of the electric current they use, strength of magnetic field they generate, mechanism which they use for controlling the fluid and fluid they control. The mechanism is different from the linear, plunger type actuator to the rocket actuators and pivoted armature actuators. For regulating the fluid, the valve use the design of two ports or it can use the design of three or more ports for switching flows between ports. On a manifold multiple solenoid, valves are placed together.
Invention of Solenoid Valves
ASCO Numatics in 1910 became the first company which developed and manufactured the solenoid valve. Solenoid valves are one of the most commonly used control elements in the fluidic logic. Their tasks are to release, dose, shut off, mix or distribute the fluids. Solenoid valves provide safe and fast switching, long service life, high reliability, compact design and low control power.
Operation of Solenoid Valves
There are various types of valves designs. Generally the valves have many fluid paths and ports. When solenoid is not energized and the valve is open then the valve is termed as normally open. When solenoid is not energized and the valve is closed then the valve is termed as normally closed. There are also more complicated designs like 3 – way valves. There are 3 ports in 3 – way valve, in which one port is connected to either of exhaust port or supply port.
These valves are characterized on the basis of operation. Limited force can be generated from small solenoid, if the generated force is sufficient to close and open the valve then only direct acting solenoid valve is possible.
Relationship between the fluid pressure, orifice area and the required solenoid force for the direct acting solenoid valve is
(Fs = PA =Pπd² / 4)
Where Fsis required solenoid force, P is the fluid pressure, A is the orifice area and d is the orifice diameter.
When large orifice and high pressure are encountered then high force is required and for generating those force solenoid valve design which is internally piloted may be possible. In such type of designs, for the generation of high valve force line pressure is used and the use of line pressure is controlled by a small solenoid.
Internally piloted valves are used when the fluid is water like in irrigation systems and dishwashers and the pressure might be 550kPa and orifice diameter might be 19mm.
The solenoid in few solenoid valves act directly on main valve while some other uses complete, small solenoid valve which is called as pilot for actuating a large valve.
And the solenoid valve which is combined with pneumatically actuated valve and packaged and sold as a single unit is known as solenoid valve.
Requirement of power in piloted valves for controlling is much lessbut are slower. For open and stay open piloted valves need full power supply at all the time while the full power requirement of a direct acting solenoid valve is for short period of time for opening and consumes very low power for staying open and they can operates in 5 milliseconds to 10 milliseconds while the piloted valve operation time depends on its size (generally 15 milliseconds to 150 milliseconds).
Working of Solenoid Valve
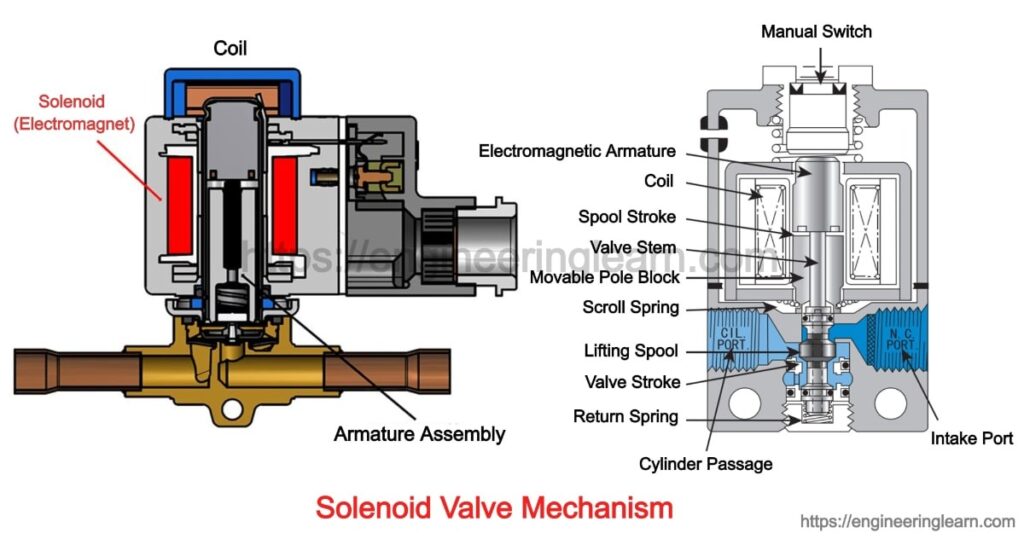
There are two main parts in solenoid valve: The Valve and the Solenoid.
The solenoid is applied to change the electrical energy into the mechanical energy which consequences to closing or opening of the valve mechanically. The solenoid valves can use rubber or metal seals and have electrical interface for allowing easy control. A spring is used for holding the valve closed or opened when the valve is not activated.
The diaphragm of the solenoid valve has a pinhole in it through its center which let a small amount of water to flow through it. This water fill the cavity present at the other side of diaphragm and balanced the pressure on both the side of diaphragm but still compressed spring exert a net downward force, but the spring is weak and can only enable to close the inlet because there is equalized pressure on both side of diaphragm. When the diaphragm close the valve then on outlet side of valve’s bottom pressure reduces and the spring are not able to holding the valve in closed position. This method of working takes place because with the help of pin which is armature of solenoid blocked the passage of small drain and are pushed downward with the help of a spring.
Pin was withdrawn with the help of magnetic force when the current is passed through solenoid the and water drain out the passage faster than pinhole can refill. Incoming pressure lifts the diaphragm as the pressure of the chamber decreases which results in opening of main valve and let the water flow directly. As the solenoid deactivated and passage get closed very little force is required by the spring for pushing the diaphragm down and then main valve closes.
Parts of Solenoid Valve
Following are the basic components of a solenoid valve:
- Solenoid Sub – Assembly ( Core, Core spring, Shading coil, Plug nut, Core tube, Solenoid coil, Retaining clip)
- Bonnet Seal – core tube
- Bonnet
- Bonnet – Diaphragm – Body Seal
- Hanger Spring
- Diaphragm
- Disk
- Backup Washer
- Valve Body
The plunger or core of the valve is magnetic component which moves when solenoid gets energized. The plug nut and the core is coaxial with solenoid. The movement of core can break or make the seals which control the fluid movement. The spring with hold the core at their normal position when coil is not energized. The core tube guides and contains the core and also retain plug nut and seal the fluid. For optimizing the core movement, core tube need to be non magnetic, it would offer shunt path for field lines if the core tube were magnetic. Core tube is an enclosed metal shell in some designs which simplify the sealing problem because from the enclosure fluid cannot escape but it increase magnetic path resistance because magnetic path traverse the thickness of core tube twice once near core and once near the plug nut.
Materials Used for the Construction of Solenoid Valves
The material used for valve body should be compatible with fluid. Generally aluminum, brass, plastic and stainless steel are the materials used for solenoid valve body. The seals should also be compatible with fluid. For making the sealing easier, the core, plug nut, shading ring, springs and other parts are also exposed to liquid so they also require to be compatible with the fluid. For passing the solenoid’s field through the core and plug nut the core tube need to be non magnetic. The core and plug nut require material which have good magnetic properties like iron (but iron is more prone to corrosion). Therefore stainless steel are used because they can be magnetic as well as non magnetic.
Types of Solenoid Valve
1. Direct Acting Valves: ( Types of Solenoid Valve )
In this type of solenoid valve there is a coil which magnetically opens the valve in direct action which lifts the shaft as well as the valve’s seat without depending on the pressure present outside. Direct – acting solenoid valves requires full power at the time of opening of valve and they can be at open state when operating at low power.
2. Pilot Operated Valves: ( Types of Solenoid Valve )
In pilot operated valves a smaller pilot valves are activated by the solenoid which opens up a large valve which is operating at very high pressure which is required in steam, hydraulics etc. and for operating greater volume flow as well as for releasing huge quantity of gases, steam, liquids and air. Piloted valves need very less electrical energy for their operation but still they need full power to be maintained throughout the period they are in open state but still they can perform slower than that of direct – acting solenoid valve.
3. Two Way Valves: ( Types of Solenoid Valve )
In two way valve, each of the two ports are used one by one to allow the flow and closing also. Two- way valve can be specified as normally closed or normally open in their operation. When the valve is in open state, it remains at that state until some current is applied for closing the valve. When the electric power is suspended then the valve reopens automatically. Generally closed solenoid valves are common which works in opposite manner and remains close until power source open it.
4. Three Way Valves: ( Types of Solenoid Valve )
Three way valves have three ports and are provided when exhaustive and alternative pressure are needed for the operation like for dishwasher and coffee machine.
5. Four Way Valves: ( Types of Solenoid Valve )
Four way valves are the valve which has four or more than four ports connections. They are generally used with dual acting actuator or cylinder. In Four – way valves half of the port connections are used to provide exhaust pressure and remaining half are used to provide supply pressure. These valves are specifies as normally open, normally closed or universal.
Applications of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves are used in hydraulic systems and fluid power pneumatic system for controlling the larger industrial valves or fluid power motors and cylinder. Solenoid valves are also used in automatic irrigation sprinkler with automatic controller. Dishwashers and domestic washing machines also use solenoid valves for controlling the entry of water in the machine. For actuating the carbon dioxide hammer valve solenoid valves are used in paintball gun triggers. Solenoid valves are generally called as “Solenoid”. For wide array of industrial applications solenoid valves are used like general on – off control, pilot plant control loops, process control systems, calibration and test stands and various equipment manufacturing applications.
Advantages of Solenoid Valves
- Less power consumption
- Replacement parts are cheap
- Remote operation
- Quick response time
- Compatible with AC and DC voltage
- High and low temperature usage
- Installed horizontally or vertically
Disadvantages of Solenoid Valves
Due to human errors, the valve face problems at the time when voltage become either too much or too less because it weakens or strengthen the electromagnetic field.
- It is voltage sensitive.
- During operation, the control system must stay on.
- If the magnetic field does not set up correctly then the solenoid valve can partly close.
- Over the lifetime of the valve, the coil of the valve needs to be replaced.
- Flow through the valve can be affected by the fluid flowing (backflow is always less than the pre valve flow).